Volume 16, Number 11—November 2010
Research
Comparison of 3 Infrared Thermal Detection Systems and Self-Report for Mass Fever Screening
Figure 2
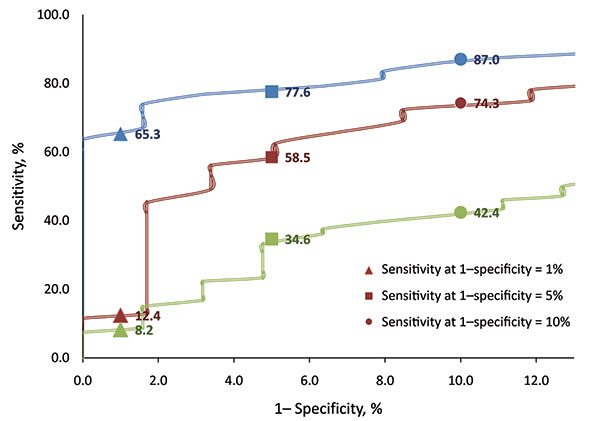
Figure 2. Enhanced view of receiver operating characteristic curves of 3 infrared thermal detection systems for detecting fever (oral temperature >100°F) showing sensitivities at false-positive rates (FPR) of 1%, 5%, and 10%. Red, FLIR ThermoVision A20M (FLIR Systems Inc., Boston, MA, USA); blue, OptoTherm Thermoscreen (OptoTherm Thermal Imaging Systems and Infrared Cameras Inc., Sewickley, PA, USA); and green, Wahl Fever Alert Imager HSI2000S (Wahl Instruments Inc., Asheville, NC, USA).
Page created: March 08, 2011
Page updated: March 08, 2011
Page reviewed: March 08, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.