Volume 16, Number 12—December 2010
Research
Reassortant Group A Rotavirus from Straw-colored Fruit Bat (Eidolon helvum)
Figure 1
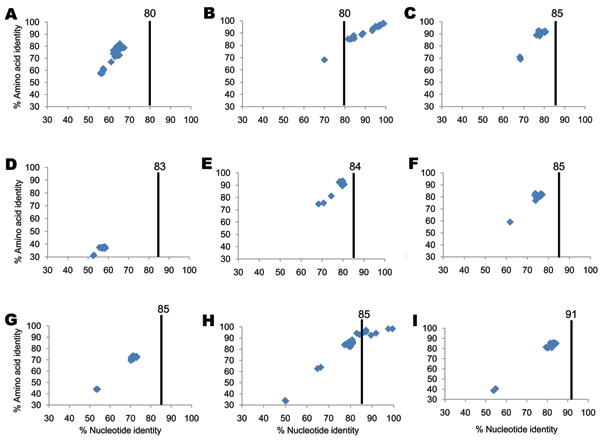
Figure 1. Percentage nucleotide and deduced amino acid homologies of A) viral protein 7 (VP7), B) VP4, C) VP6, D) VP1, E) VP2, F) nonstructural protein 2 (NSP2), G) NSP3, H) NSP4, and I) NSP5 gene segments of bat rotavirus strain Bat/KE4852/07 from Kenya compared with respective genes deposited in GenBank. Vertical lines indicate nucleotide percentage identity cutoff values defining genotypes for 11 rotavirus gene segments (7,10). Blue diamonds indicate coordinates for each pairwise comparison when percentage nucleotide identity is plotted against percentage amino acid identity. GenBank accession numbers used in this comparison are listed in the Technical Appendix.
References
- Ramig RF, Ciarlet M, Mertens PP, Dermody TS. Genus rotavirus. In: Fauquet C, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA, editors. Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses: eighth report of the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses. San Diego (CA): Elsevier Academic Press; 2005. p. 484–96.
- Parashar UD, Gibson CJ, Bresee JS, Glass RI. Rotavirus and severe childhood diarrhea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:304–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Estes MK, Kapikian A. Rotaviruses In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, et al., editors. Fields virology, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Kluwer/Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2007. p. 1917–74.
- Matthijnssens J, Rahman M, Martella V, Xuelei Y, De Vos S, De Leener K, Full genomic analysis of human rotavirus strain B4106 and lapine rotavirus strain 30/96 provides evidence for interspecies transmission. J Virol. 2006;80:3801–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brüssow H, Nakagomi O, Gerna G, Eichhorn W. Isolation of an avian-like group-A rotavirus from a calf with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:67–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Heiman E, Arijs I, Delbeke T, McDonald SM, Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J Virol. 2008;82:3204–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martella V, Banyai K, Matthijnssens J, Buonavoglia C, Ciarlet M. Zoonotic aspects of rotaviruses. Vet Microbiol. 2010;140:246–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matthijnssens J, Bilcke J, Ciarlet M, Martella V, Banyai K, Rahman M, Rotavirus disease and vaccination: impact on genotype diversity. Future Microbiol. 2009;4:1303–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Rahman M, Attoui H, Banyai K, Estes MK, Recommendations for the classification of group A rotaviruses using all 11 genomic RNA segments. Arch Virol. 2008;153:1621–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:531–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swanepoel R, Leman PA, Burt FJ, Zachariades NA, Braack LE, Ksiazek TG, Experimental inoculation of plants and animals with Ebola virus. Emerg Infect Dis. 1996;2:321–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tong S, Conrardy C, Ruone S, Kuzmin IV, Guo XL, Tao Y, Detection of novel SARS-like and other coronaviruses in bats from Kenya. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:482–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kuzmin IV, Niezgoda M, Franka R, Agwanda B, Markotter W, Beagley JC, Lagos bat virus in Kenya. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:1451–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kemp GE, Le Gonidec G, Karabatsos N, Rickenbach A, Cropp CB. IFE: a new African orbivirus isolated from Eidolon helvum bats captured in Nigeria, Cameroon and the Central African Republic [in French]. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 1988;81:40–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Iturriza Gómara M, Wong C, Blome S, Desselberger U, Gray J. Molecular characterization of VP6 genes of human rotavirus isolates: correlation of genogroups with subgroups and evidence of independent segregation. J Virol. 2002;76:6596–601. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Das BK, Gentsch JR, Cicirello HG, Woods PA, Gupta A, Ramachandran M, Characterization of rotavirus strains from newborns in New Delhi, India. J Clin Microbiol. 1994;32:1820–2.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gentsch JR, Glass RI, Woods P, Gouvea V, Gorziglia M, Flores J, Identification of group A rotavirus gene 4 types by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:1365–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gouvea V, Glass RI, Woods P, Tanguchi K, Clark HF, Forrester B, Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990;28:276–82.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB. GeneDoc: a tool for editing and annotating multiple sequence alignments, version 2.7.000. Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center’s National Resource for Biomedical Supercomputing; 1997 [cited 2010 Sep 2]. http://www.nrbsc.org/downloads/
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–402. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:754–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1572–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W465–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dyall-Smith ML, Lazdins I, Tregear GW, Holmes IH. Location of the major antigenic sites involved in rotavirus serotype-specific neutralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:3465–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McDonald SM, Aguayo D, Gonzalez-Nilo FD, Patton JT. Shared and group-specific features of the rotavirus RNA polymerase reveal potential determinants of gene reassortment restriction. J Virol. 2009;83:6135–48. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gentsch JR, Laird AR, Bielfelt B, Griffin DD, Banyai K, Ramachandran M, Serotype diversity and reassortment between human and animal rotavirus strains: implications for rotavirus vaccine programs. J Infect Dis. 2005;192:S146–59. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dennehy PH. Rotavirus vaccines: an overview. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008;21:198–208. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fitzgerald TA, Munoz M, Wood AR, Snodgrass DR. Serological and genomic characterisation of group A rotaviruses from lambs. Arch Virol. 1995;140:1541–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gouvea V, Lima RC, Linhares RE, Clark HF, Nosawa CM, Santos N. Identification of two lineages (WA-like and F45-like) within the major rotavirus genotype P [8]. Virus Res. 1999;59:141–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ulukanligil M, Seyrick A, Asian G, Ozbilge H, Atay S. Environmental pollution with soil-transmitted helminths in Sanliurfa, Turkey. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2001;96:903–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Muttalib MA, Huq HM, Huq JA, Suzuki N. Soil pollution with Ascaris eggs in three villages of Bangladesh. In: Yokogawa M, editor. Collected papers on the control of soil-transmitted helminthiasis. Vol. II. Tokyo: APCO; 1983. p. 66–71.
- Nyarango RM, Kabiru EW, Nyanchongi BO. The risk of pathogenic intestinal parasite infections in Kisii Municipality, Kenya. BMC Public Health. 2008;8:237–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ferreira FF, Guimaraes FR, Fumian TM, Victoria M, Vieira CB, Luz S, Environmental dissemination of group A rotavirus: P-type, G-type and subgroup characterization. Water Sci Technol. 2009;60:633–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rutjes SA, Lodder WJ, van Leeuwen AD, de Roda Husman AM. Detection of infectious rotavirus in naturally contaminated source waters for drinking water production. J Appl Microbiol. 2009;107:97–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bergmans W. Review of drinking behaviour of African fruit bats (Mammalia: Megachiroptera). Bulletin of the Carnegie Museum of Natural History. 1978;6:20–5.
- Nagashima S, Kobayashi N, Ishino M, Alam MM, Ahmed MU, Paul SK, Whole genomic characterization of a human rotavirus strain B219 belonging to a novel group of the genus Rotavirus. J Med Virol. 2008;80:2023–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parashar UD, Hummelman EG, Bresee JS, Miller MA, Glass RI. Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:565–72.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wildlife Conservation Society. Conference summary. One World One Health: Building Interdisciplinary Bridges to Health in a Globalized World, 2004 [cited 2010 Sep 2]. http://www.oneworldonehealth.org/sept2004/owoh_sept04.html
Page created: August 29, 2011
Page updated: August 29, 2011
Page reviewed: August 29, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.