Volume 16, Number 6—June 2010
Dispatch
Vaccinia Virus Infection in Monkeys, Brazilian Amazon
Figure
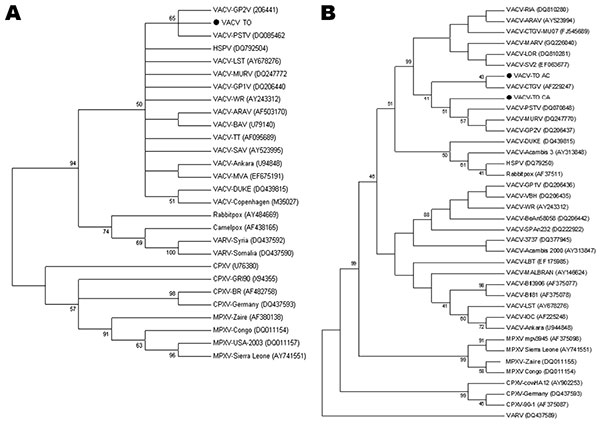
Figure. Consensus bootstrap phylogenetic trees based on nucleotide sequences of orthopoxvirus vaccinia growth factor (vgf) (A) and hemagglutinin (ha) (B) genes. Trees were constructed with ha or vgf sequences by using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates and the Tamura 3-parameter model in MEGA version 3.1 software (www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values >40% are shown. Nucleotide sequences were obtained from GenBank. Black dots indicate vaccinia virus (VACV) obtained from Cebus apella (VACV-TO CA) and Allouata caraya (VACV AC). All vgf sequences obtained from monkey serum samples showed 100% and are represented as a unique sequence in the vgf tree (VACV TO). HSPV, horsepoxvirus; VARV, variola virus; CPXV, cowpoxvirus; MPXV, monkeypoxvirus.