Volume 17, Number 3—March 2011
Research
Amplification of Emerging Viruses in a Bat Colony
Figure 2
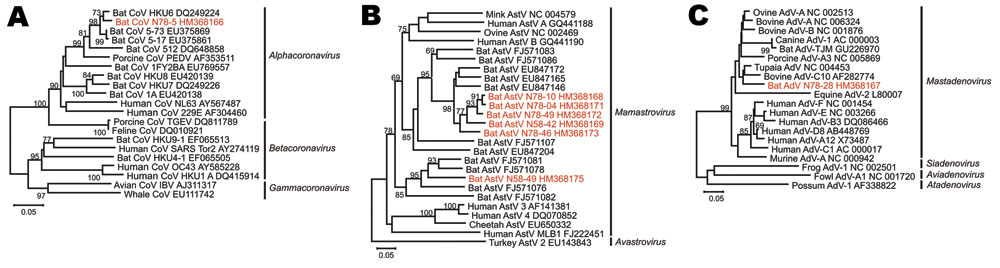
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of novel bat viruses. A) Coronavirus, B) astrovirus, C) adenovirus. Neighbor-joining phylogenies were generated with MEGA (www.megasoftware.net), by using an amino acid percentage distance substitution model drawn to scale, complete deletion option, and 1,000 bootstrap reiterations. Bootstrap values are shown next to the branches; values <65 were removed for graphic reasons. Viruses newly identified in this study are shown in red. Viral genera are depicted next to taxon names. The BLOSUM aligned datasets corresponded to an 816-nt alignment, corresponding to nucleotides 14,781–15,596 in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) strain Tor2 (GenBank accession no. AY274119) for CoVs (A); a 381-nt alignment corresponding to nt 3,437–3,817 in mink astrovirus (AstV) (GenBank NC_004579) for AstVs (B); and to a 255-nt alignment corresponding to nt 46–300 in the bovine adenovirus (AdV) C10 hexon gene (GenBank accession no. AF282774) for AdVs (C). Trees were visualized in MEGA4, with prototype virus sequences restricted to ≈20 taxa additional to newly identified viruses for graphic reasons. Scale bars indicate amino acid substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.