Volume 17, Number 6—June 2011
Dispatch
Immunologic Changes during Pandemic (H1N1) 2009, China
Figure 2
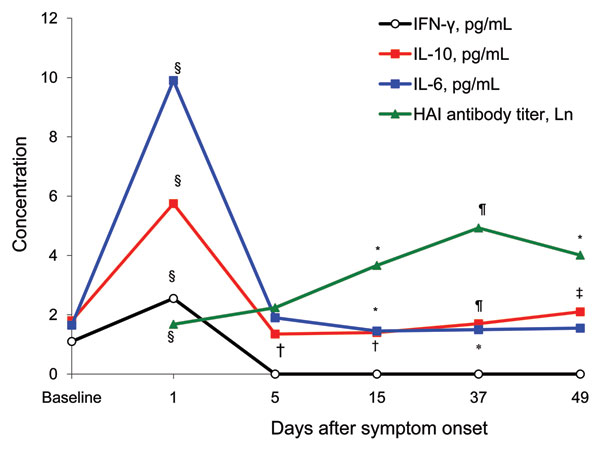
Figure 2. Serum cytokine concentrations and hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) antibody titers of 28 patients with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 during hospitalization and the follow-up period 15, 37, and 49 days after symptom onset, China. Serum concentrations of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-10 (IL-10), and IL-6 are medians (pg/mL). Serum HAI antibody titers were transformed by using the natural logarithm and are shown as means. Baseline cytokine concentrations on the y-axis are values for healthy persons. *p<0.05 when IL-6 or HAI antibody levels were compared with those at day 5; †p<0.05 when IL-10 level was compared with those at baseline; ‡p<0.05 when IL-10 level was compared with those at days 5 or 15; §p<0.05 when value was compared with that at any other time point; ¶p<0.05 when value was compared with those at days 5, 15, or 49.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.