Volume 18, Number 10—October 2012
Dispatch
Influenza Virus Infection in Nonhuman Primates
Figure 2
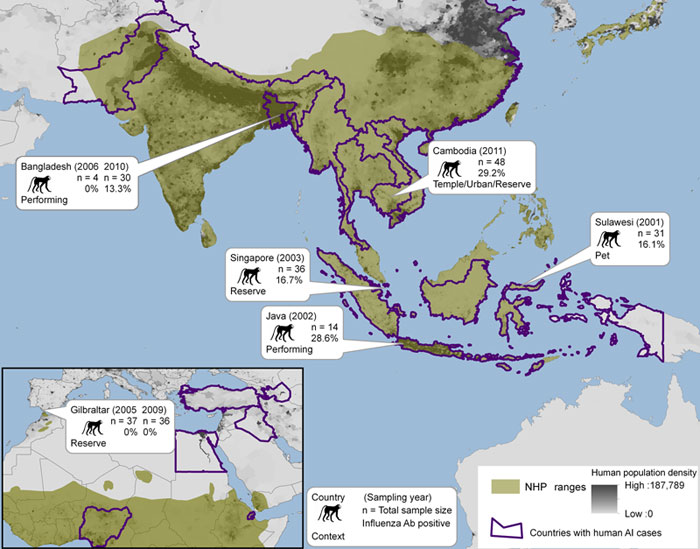
Figure 2. . . . . Nonhuman primate (NHP) habitat countries (in green) and approximate location of sampling sites, with sample size, year collected, context of human–macaque interaction, and seroprevalence of antibodies against influenza virus A. Countries that have reported human influenza infection of avian origin (AI) are outlined in purple.
Page created: September 13, 2012
Page updated: September 13, 2012
Page reviewed: September 13, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.