Volume 18, Number 3—March 2012
Dispatch
Poultry Culling and Campylobacteriosis Reduction among Humans, the Netherlands
Figure 2
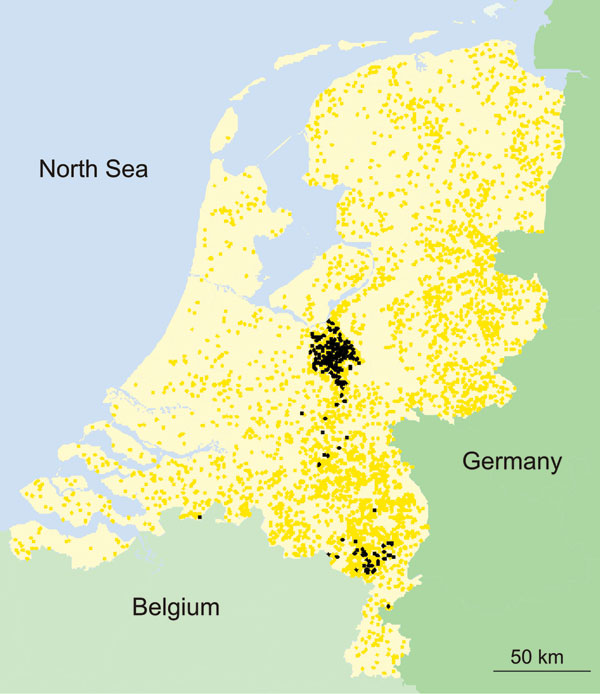
Figure 2. Locations of all 5,360 commercial poultry farms in the Netherlands (2). Black dots indicate farms that were infected during the 2003 epidemic of avian influenza; yellow dots indicate farms that were not infected.
References
- Stegeman A, Bouma A, Elbers ARW, De Jong MCM, Nodelijk G, De Klerk F, Avian influenza a virus (H7N7) epidemic in the Netherlands in 2003: course of the epidemic and effectiveness of control measures. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:2088–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boender GJ, Hagenaars TJ, Bouma A, Nodelijk G, Elbers AR, de Jong MC, Risk maps for the spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza in poultry. PLOS Comput Biol. 2007;3:e71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Pelt W, Mevius D, Stoelhorst HG, Kovats S, van de Giessen AW, Wannet W, A large increase of Salmonella infections in 2003 in the Netherlands: hot summer or side effect of the avian influenza outbreak? Euro Surveill. 2004;9:17–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Widdowson MA, Bosman A, Van Straten E, Tinga M, Chaves S, Van Eerden L, Automated, laboratory-based system using the Internet for disease outbreak detection, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:1046–52.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- GfK Panel Services Benelux. ConsumerScan [cited 2011 Feb 9]. http://www.gfk.com/ps_benelux/instruments/consumerscan/index.nl.html
- Olson CK, Ethelberg S, Van Pelt W, Tauxe RV. Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni infections in industrialized nations. In: Nachamkin I, Szymanski CM, Blaser MJ, editors. Campylobacter. Washington: ASM Press; 2008. p. 163–89.
- Ogden ID, Dallas JF, MacRae M, Rotariu O, Reay KW, Leitch M, Campylobacter excreted into the environment by animal sources: prevalence, concentration shed, and host association. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009;6:1161–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ethelberg S, Simonsen J, Gerner-Smidt P, Olsen KEP, Molbak K. Spatial distribution and registry-based case–control analysis of Campylobacter infections in Denmark, 1991–2001. Am J Epidemiol. 2005;162:1008–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Garrett N, Devane ML, Hudson JA, Nicol C, Ball A, Klena JD, Statistical comparison of Campylobacter jejuni subtypes from human cases and environmental sources. J Appl Microbiol. 2007;103:2113–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hald B, Skovgard H, Pedersen K, Bunkenborg H. Influxed insects as vectors for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Danish broiler houses. Poult Sci. 2008;87:1428–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sproston EL, Ogden ID, MacRae M, Forbes KJ, Dallas JF, Sheppard SK, Multi-locus sequence types of Campylobacter carried by flies and slugs acquired from local ruminant faeces. J Appl Microbiol. 2010;109:829–38. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wilson IG. Airborne Campylobacter infection in a poultry worker: case report and review of the literature. Commun Dis Public Health. 2004;7:349–53.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bull SA, Allen VM, Domingue G, Jorgensen F, Frost JA, Ure R, Sources of Campylobacter spp. colonizing housed broiler flocks during rearing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72:645–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hendricks M. Ellen Silbergeld: resistance fighter. 2002 [cited 2011 Jan 28]. http://www.jhsph.edu/Publications/Spring02/features.htm
- Vellinga A, Van Loock F. The dioxin crisis as experiment to determine poultry-related Campylobacter enteritis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:19–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 17, 2012
Page updated: February 17, 2012
Page reviewed: February 17, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.