Volume 18, Number 3—March 2012
Research
Using Genotyping and Geospatial Scanning to Estimate Recent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Transmission, United States
Figure 2
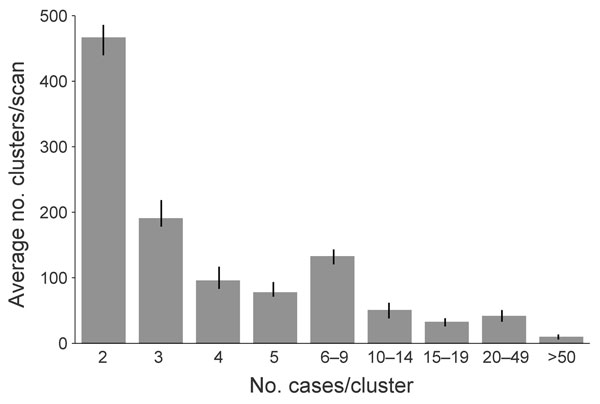
Figure 2. Frequency of genotype clusters of tuberculosis, by cluster size (mean 5.68, median 3, range: 2–173), United States, 2005–2009. Frequency was determined by using SaTScan version 9.1.0 (26) on the basis of 3 consecutive, overlapping years: scan A, 2005–2007 (n = 970); scan B, 2006–2008 (n = 1,019); scan C, 2007–2009 (n = 1,128). Error bars indicate upper and lower limits of clusters identified between scan periods.
References
- Buff AM, Moonan PK, Desai MA, McKenna TL, Harris DA, Rogers BJ, South Carolina tuberculosis genotype cluster investigation: a tale of substance abuse and recurrent disease. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010;14:1347–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pevzner ES, Robison S, Donovan J, Allis D, Spitters C, Friedman R, Tuberculosis transmission and use of methamphetamines in Snohomish County, WA, 1991–2006. Am J Public Health. 2010;100:2481–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burman WJ, Bliven EE, Cowan L, Bozeman L, Nahid P, Diem L, Relapse associated with active disease caused by Beijing strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1061–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jasmer RM, Bozeman L, Schwartzman K, Cave MD, Saukkonen JJ, Metchock B, Recurrent tuberculosis in the United States and Canada: relapse or reinfection? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170:1360–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lai CC, Tan CK, Lin SH, Liao CH, Chou CH, Huang YT, Molecular evidence of false–positive cultures for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a Taiwanese hospital with a high incidence of TB. Chest. 2010;137:1065–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cook VJ, Stark G, Roscoe DL, Kwong A, Elwood RK. Investigation of suspected laboratory cross–contamination: interpretation of single smear–negative, positive cultures for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12:1042–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Monitoring tuberculosis programs–National Tuberculosis Indicator Project, United States, 2002–2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010;59:295–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barnes PF, Cave MD. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1149–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cronin WA, Golub JE, Lathan MJ, Mukasa LN, Hooper N, Razeq JH, Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in a low- to moderate-incidence state: are contact investigations enough? Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:1271–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clark CM, Driver CR, Munsiff SS, Driscoll JR, Kreiswirth BN, Zhao B, Universal genotyping in tuberculosis control program, New York City, 2001–2003. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:719–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Serpa JA, Teeter LD, Musser JM, Graviss EA. Tuberculosis disparity between US–born blacks and whites, Houston, Texas, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:899–904. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ellis BA, Crawford JT, Braden CR, McNabb SJ, Moore M, Kammerer S, Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in a sentinel surveillance population. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:1197–209.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Soolingen D, Borgdorff MW, de Haas PE, Sebek MM, Veen J, Dessens M, Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in the Netherlands: a nationwide study from 1993 through 1997. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:726–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barnes PF, Yang Z, Pogoda JM, Preston-Martin S, Jones BE, Otaya M, Foci of tuberculosis transmission in central Los Angeles. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:1081–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Small PM, Hopewell PC, Singh SP, Paz A, Parsonnet J, Ruston DC, The epidemiology of tuberculosis in San Francisco. A population–based study using conventional and molecular methods. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1703–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Murray M, Alland D. Methodological problems in the molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;155:565–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Houben RM, Glynn JR. A systematic review and meta-analysis of molecular epidemiological studies of tuberculosis: development of a new tool to aid interpretation. Trop Med Int Health. 2009;14:892–909. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fok A, Numata Y, Schulzer M, FitzGerald MJ. Risk factors for clustering of tuberculosis cases: a systematic review of population-based molecular epidemiology studies. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12:480–92.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulldorff M, Nagarwalla N. Spatial disease clusters: detection and inference. Stat Med. 1995;14:799–810. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ghosh S, Moonan PK, Cowan L, Grant J, Kammerer S, Navin TR. Tuberculosis genotyping information management system: enhancing tuberculosis surveillance in the United States. Infect Genet Evol. 2011 Oct 25; [Epub ahead of print]. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Reported tuberculosis in the United States, 2009. Atlanta: US.Department of Health and Human Services; October 2010 [cited 2012 Jan 12]. http://www.cdc.gov/tb/statistics/reports/2010/default.htm
- Cowan LS, Diem L, Monson T, Wand P, Temporado D, Oemig TV, Evaluation of a two–step approach for large–scale, prospective genotyping of Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:688–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Click ES, Moonan PK, Winston CA, Cowan LS, Oeltmann JE. Relationship between Mycobacterium tuberculosis phylogenetic lineage and clinical site of disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:211–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oeltmann JE, Kammerer JS, Pevzner ES, Moonan PK. Tuberculosis and substance abuse in the United States, 1997–2006. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:189–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulldorff M. A spatial scan statistic. Comm Statist Theory Methods. 1997;26:1481–96. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Kulldorff M; Information Management Services, Inc. SaTScanTM v8.0: Software for the spatial and space-time scan statistics [cited 10 Jan 2012]. http://www.satscan.org/
- United States Census Bureau. Census geographic regions.[cited 2011 Oct 18]. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/geo_defn.html#CensusRegion
- Miller AC, Sharnprapai S, Suruki R, Corkren E, Nardell EA, Driscoll JR, Impact of genotyping of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on public health practice in Massachusetts. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:1285–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vanhomwegen J, Kwara A, Martin M, Gillani FS, Fontanet A, Mutungi P, Impact of immigration on the molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in Rhode Island. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:834–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glynn JR, Crampin AC, Yates MD, Traore H, Mwaungulu FD, Ngwira BM, The importance of recent infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in an area with high HIV prevalence: a long-term molecular epidemiological study in Northern Malawi. J Infect Dis. 2005;192:480–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lathan M, Mukasa LN, Hooper N, Golub J, Baruch N, Mulcahy D, Cross-jurisdictional transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Maryland and Washington, DC, 1996–2000, linked to the homeless. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:1249–51.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Geng E, Kreiswirth B, Driver C, Li J, Burzynski J, DellaLatta P, Changes in the transmission of tuberculosis in New York City from 1990 to 1999. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1453–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nava-Aguilera E, Andersson N, Harris E, Mitchell S, Hamel C, Shea B, Risk factors associated with recent transmission of tuberculosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009;13:17–26.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Story A, Murad S, Roberts W, Verheyen M, Hayward AC; London Tuberculosis Nurses Network. Tuberculosis in London: the importance of homelessness, problem drug use and prison. Thorax. 2007;62:667–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weis S. Contact investigations: how do they need to be designed for the 21st century? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:1016–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taylor Z. Guidelines for the investigation of contacts of persons with infectious tuberculosis. Recommendations from the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association and CDC. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2005;54(RR-15):1–81.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Asghar RJ, Patlan DE, Miner MC, Rhodes HD, Solages A, Katz DJ, Limited utility of name-based tuberculosis contact investigations among persons using illicit drugs: results of an outbreak investigation. J Urban Health. 2009;86:776–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perri BR, Proops D, Moonan PK, Munsiff SS, Kreiswirth BN, Kurepina N, Mycobacterium tuberculosis cluster with developing drug resistance, New York, New York, USA, 2003–2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:372–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schürch AC, Kremer K, Kiers A, Daviena O, Boeree MJ, Siezen RJ, The tempo and mode of molecular evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis at patient-to-patient scale. Infect Genet Evol. 2010;10:108–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Supply P, Allix C, Lesjean S, Cardoso-Oelemann M, Rusch-Gerdes S, Willery E, Proposal for standardization of optimized mycobacterial interspersed repetitive unit–variable-number tandem repeat typing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:4498–510. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 16, 2012
Page updated: February 16, 2012
Page reviewed: February 16, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.