Volume 18, Number 4—April 2012
Dispatch
Genomic Analysis of emm59 Group A Streptococcus Invasive Strains, United States
Figure
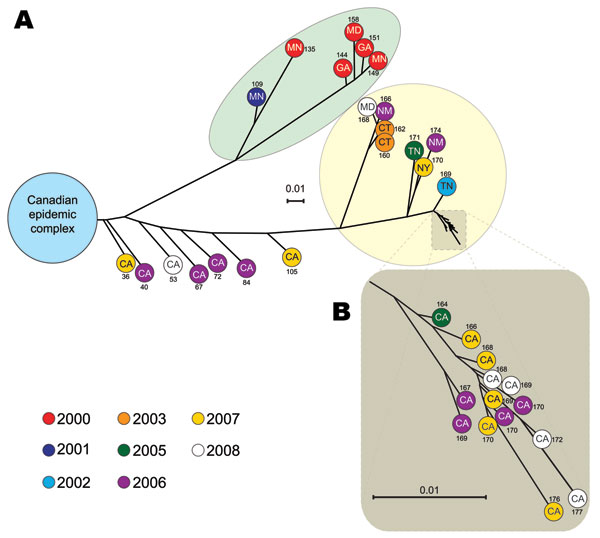
Figure. Inferred genetic relationships among 40 emm59 group A Streptococcus (GAS) strains isolated in the United States during 2000–2009, based on 635 concatenated single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci identified by whole-genome sequencing. A) Phylogenetic tree showing that most of the strains are genetically distinct from an emm59 GAS clone responsible for >500 cases of invasive disease in Canada. Light green highlight indicates older (US) strains (isolated during 2000–2001) that form 1 clearly differentiated branch of the phylogenetic tree. Yellow highlighting indicates a second lineage isolated in the United States (CA, CT, NM, NY, and TN) during 2003–2008. Circles represent individual isolates. The number of SNPs separating each isolate from strain MGAS15252 from Canada is indicated. Five strains (2 from MN, 2 from CA, and 1 from OR; not represented individually in the phylogenetic tree) are members of the epidemic complex from Canada. B) Magnification of the phylogenetic tree showing a conspicuous discrete clonal complex formed by 14 strains isolated in the San Francisco Bay area during 2005–2008. Genome-wide, these 14 strains are separated by an average of 10 SNPs. CA, California; CT, CT, Connecticut; GA, Georgia; MD, Maryland; MN, Minnesota; NM, New Mexico; NY, New York; TN, Tennessee. A matrix displaying the total number of core genome SNPs separating each individual strain from any other is available in .