Volume 18, Number 7—July 2012
Dispatch
Dobrava Hantavirus Infection Complicated by Panhypopituitarism, Istanbul, Turkey, 2010
Figure 1
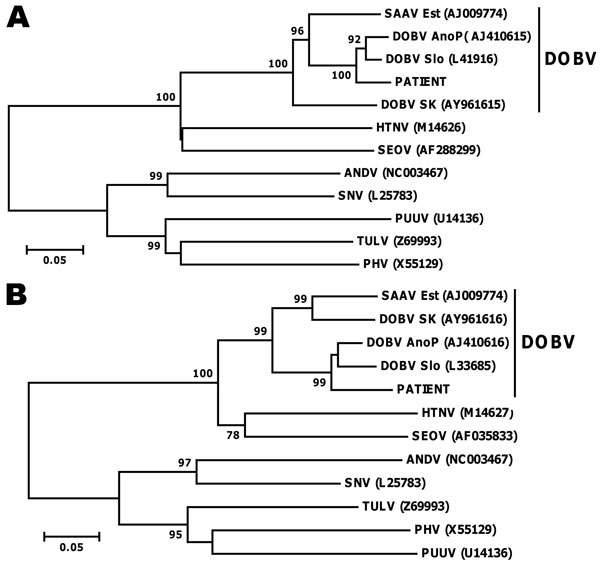
Figure 1. . . Molecular phylogenetic analysis of small (S) and medium (M) gene segments. Consensus neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree (Tamura-Nei 93 evolutionary model) of hantavirus strains was constructed as described (9) based on partial sequences of the S (panel A) and M segment (panel B). Bootstrap values >70%, calculated from 10,000 replicates, are shown at the tree branches. Sequences taken from GenBank are indicated by their accession numbers. SAAV Est, Saaremaa virus from Estonia; DOBV AnoP, Dobrava-Belgrade virus (lineage DOBV-Af) from Greece; DOBV Slo, Dobrava-Belgrade virus (lineage DOBV-Af) from Slovenia; DOB SK, Dobrava-Belgrade virus (lineage DOBV-Aa) from Slovakia; HTNV, Hantaan virus; SEOV, Seoul virus; ANDV, Andes virus; SNV, Sin nombre virus; PUUV, Puumala virus; TULV, Tula virus; PHV, Prospect Hill virus. Scale bars indicate an evolutionary distance of 0.1 substitutions per position.
References
- Clement J, Maes P, Lagrou K, Van Ranst M, Lameire N. A unifying hypothesis and a single name for a complex globally emerging infection: hantavirus disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;31:1–5.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hautala T, Sironen T, Vapalahti O, Paakko E, Sarkioja T, Salmela PI, Hypophyseal hemorrhage and panhypopituitarism during Puumala virus infection: magnetic resonance imaging and detection of viral antigen in the hypophysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:96–101. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pekic S, Cvijovic G, Stojanovic M, Kendereski A, Micic D, Popovic V. Hypopituitarism as a late complication of hemorrhagic fever. Endocrine. 2005;26:79–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hautala T, Mahonen SM, Sironen T, Hautala N, Paakko E, Karttunen A, Central nervous system–related symptoms and findings are common in acute Puumala hantavirus infection. Ann Med. 2010;42:344–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mäkelä S, Jaatinen P, Miettinen M, Salmi J, Ala-Houhala I, Huhtala H, Hormonal deficiencies during and after Puumala hantavirus infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010;29:705–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kavukçu S, Türkmen M, Salman S, Soylu S, Çamsari S. What is the risk of nephropathy associated with hantavirus in Agean region. Turkish Nephrology. Dialysis and Transplantation Journal. 1997;3:131–5.
- Çelebi G, Pişkin N, Öktem MA, İrkörücü O, Uğur AK, Öztoprak N, Anatomy of a hantavirus outbreak in Turkey. In: 14th Turkish Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Congress (KLİMİK 2009), Antalya, Turkey, March 25–29, 2009. p. 163.
- Oncul O, Atalay Y, Onem Y, Turhan V, Acar A, Uyar Y, Hantavirus infection in Istanbul, Turkey. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:303–4..PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Laakkonen J, Kallio-Kokko H, Oktem MA, Blasdell K, Plyusnina A, Niemimaa J, Serological survey for viral pathogens in Turkish rodents. J Wildl Dis. 2006;42:672–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Klempa B, Tkachenko EA, Dzagurova TK, Yunicheva YV, Morozov VG, Okulova NM, Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by 2 lineages of Dobrava hantavirus, Russia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:617–25.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kruger DH, Klempa B. Dobrava-Belgrade virus. In: Liu D, editor. Molecular detection of human viral pathogens. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; 2011. p. 629–36.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.