Volume 18, Number 8—August 2012
Dispatch
Klebsiella pneumoniae in Gastrointestinal Tract and Pyogenic Liver Abscess
Figure 1
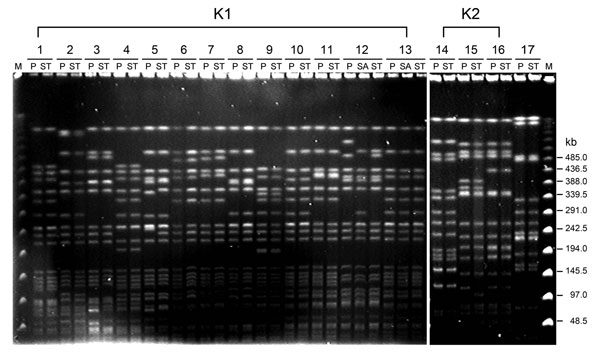
Figure 1. . Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of randomly selected isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from 17 patients with liver abscess, Taiwan, January 2009–December 2010. DNA fragments were subjected to electrophoresis after digestion with XbaI. Lanes 1–13, serotype K1 isolates; lanes 14–16, serotype K2 isolates; lane 17, serotype non-K1/K2 isolates. M, molecular mass marker; P, liver aspirate; ST, stool; SA, saliva.
Page created: July 30, 2012
Page updated: July 30, 2012
Page reviewed: July 30, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.