Volume 18, Number 8—August 2012
Dispatch
New Variants of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus, China, 2011
Figure 2
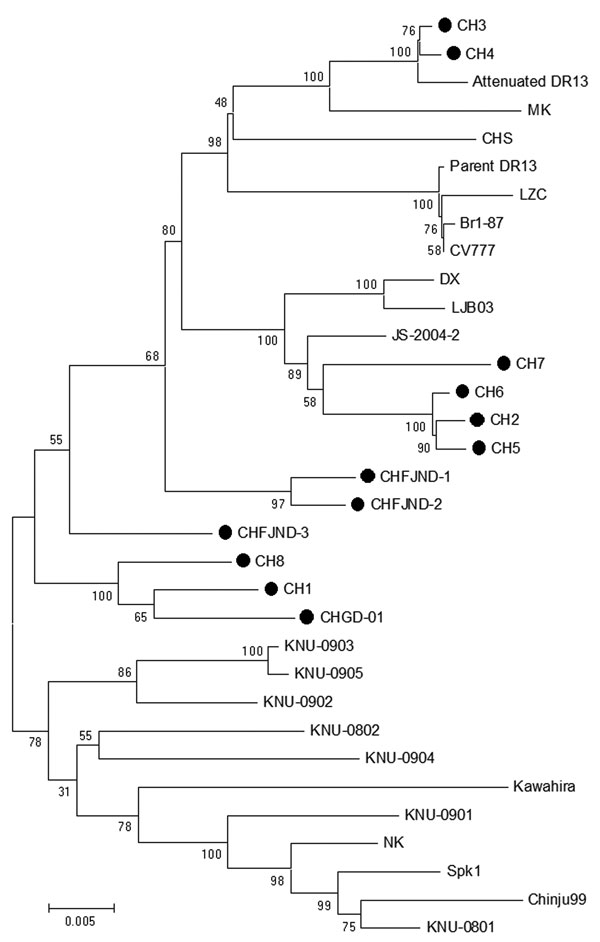
Figure 2. . Phylogenetic trees of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) strains generated by the neighbor-joining method with nucleotide sequences of the full-length spike genes. Bootstrapping with 1,000 replicates was performed to determine the percentage reliability for each internal node. Horizontal branch lengths are proportional to genetic distances between PEDV strains. Black circles indicate PEDV field isolates from the 2011 outbreak in China. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: July 19, 2012
Page updated: July 19, 2012
Page reviewed: July 19, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.