Volume 19, Number 2—February 2013
Dispatch
Transmission and Maintenance Cycle of Bartonella quintana among Rhesus Macaques, China
Figure 2
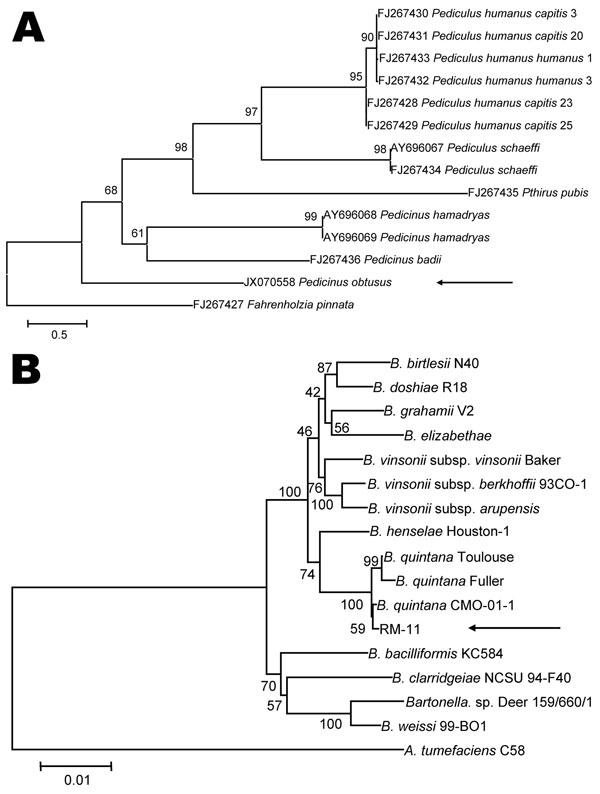
Figure 2. . Phylogenetic analyses of louse species and Bartonella spp. A) Phylogenetic tree of louse species based on the partial Cytb sequence (364-bp), obtained by using the neighbor-joining method with maximum composite likelihood analysis and bootstrap analysis of 1,000 replicates. Arrow indicates the Pedicinus obtusus louse identified in this study. The tree was rooted with the louse species Fahrenholzia pinnata. Numbers shown at each node indicate percentage of replicates that reproduced the topology of each clade. Scale bar indicates estimated evolutionary distance of 0.5 substitutions per position. B) Phylogenetic tree of Bartonella spp. based on the combined RNase P RNA, 16S, and 23S rRNA sequence alignment (4131-bp), obtained by using the same analytical method as described in panel A. Arrow indicates the RM-11 isolate. The tree was rooted with the louse species Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The GenBank accession numbers of Bartonella strains used for phylogenetic analysis are shown in Technical Appendix Table 2. Scale bar indicates estimated evolutionary distance of 0.01 substitutions per position.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.