Volume 19, Number 4—April 2013
Research
Transmission of Hepatitis E Virus from Rabbits to Cynomolgus Macaques
Figure
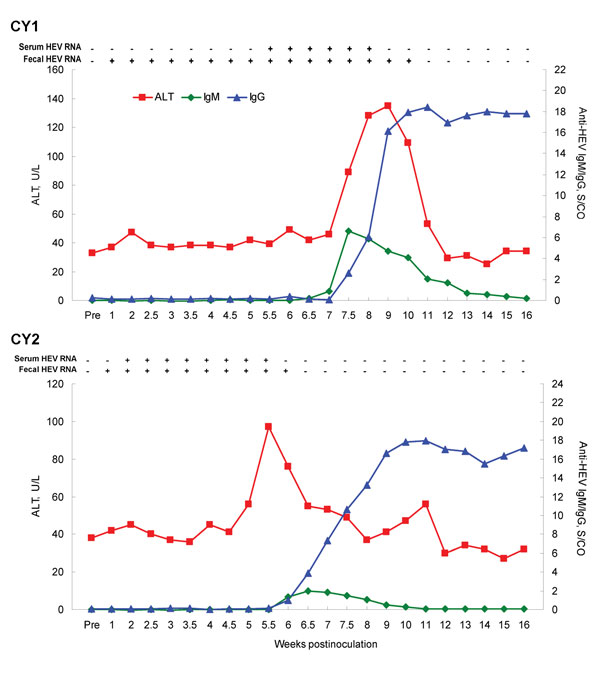
Figure. . . Cross-species transmission of rabbit hepatitis E virus (HEV) to 2 cynomolgus macaques (Cy1 and Cy2). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels are plotted as U/L. The baseline ALT levels were 33 U/L and 38 U/L for Cy1 and Cy2, respectively. The titers of HEV IgM and IgG are plotted as ELISA signal-to-cutoff (S/CO) values. Presence and absence of HEV RNA in serum or feces are indicated by + and – signs, respectively.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 13, 2013
Page updated: March 13, 2013
Page reviewed: March 13, 2013
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.