Volume 20, Number 1—January 2014
Dispatch
Novel Avian Coronavirus and Fulminating Disease in Guinea Fowl, France
Figure 1
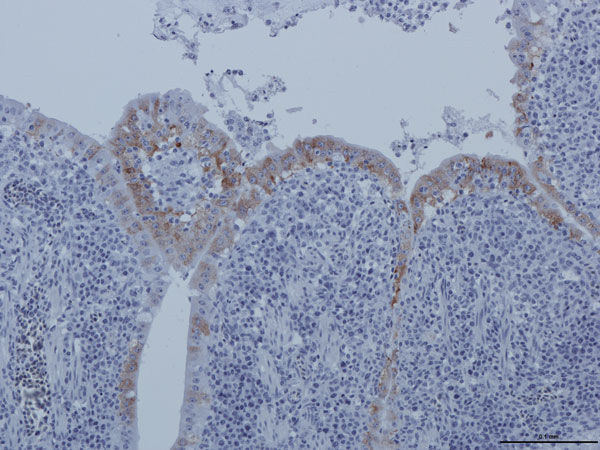
Figure 1. . . Replication of guinea fowl coronavirus in intestinal epithelium cells of experimentally infected birds as evidenced by immunohistochemical testing with a turkey coronavirus–specific monoclonal antibody, France, 2010–2011 (9). Scale bar indicates 0.1mm.
References
- Brahem A, Demarquez N, Beyrie M, Vuillaume A, Fleury HJ. A highly virulent togavirus-like agent associated with the fulminating disease of guinea fowl. Avian Dis. 1992;36:143–8 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Andral B, Lagadic M, Louzis C, Guillou JP, Gourreau JM. Fulminating disease in guinea fowl: etiological investigation. Point Veterinaire. 1987;19:515–20.
- Toffan A, Catania S, Salviato A, De Battisti C, Vascellari M, Toson M, Experimental infection of poults and guinea fowl with genetically distinct avian astroviruses. Avian Pathol. 2012;41:429–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Boheemen S, de Graaf M, Lauber C, Bestebroer TM, Raj VS, Zaki AM, Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans. MBio. 2012;3:e00473–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gouilh MA, Puechmaille SJ, Gonzalez J-P, Teeling E, Kittayapong P, Manuguerra J-C. SARS-coronavirus ancestor’s foot-prints in South-East Asian bat colonies and the refuge theory. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11:1690–702. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Victoria JG, Kapoor A, Li L, Blinkova O, Slikas B, Wang C, Metagenomic analyses of viruses in stool samples from children with acute flaccid paralysis. J Virol. 2009;83:4642–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Angly FE, Willner D, Prieto-Davó A, Edwards RA, Schmieder R, Vega-Thurber R, The GAAS metagenomic tool and its estimations of viral and microbial average genome size in four major biomes. PLOS Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000593. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stephensen CB, Casebolt DB, Gangopadhyay NN. Phylogenetic analysis of a highly conserved region of the polymerase gene from 11 coronaviruses and development of a consensus polymerase chain reaction assay. Virus Res. 1999;60:181–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Breslin JJ, Smith LG, Barnes HJ, Guy JS. Comparison of virus isolation, immunohistochemistry, and reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction procedures for detection of turkey coronavirus. Avian Dis. 2000;44:624–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jackwood MW, Hall D, Handel A. Molecular evolution and emergence of avian gammacoronaviruses. Infect Genet Evol. 2012;12:1305–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maurel S, Toquin D, Briand FX, Queguiner M, Allee C, Bertin J, First full-length sequences of the S gene of European isolates reveal further diversity among turkey coronaviruses. Avian Pathol. 2011;40:179–89. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cavanagh D. Coronaviruses in poultry and other birds. Avian Pathol. 2005;34:439–48. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Woo PCY, Lau SKP, Lam CSF, Lau CCY, Tsang AKL, Lau JHN, Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus Deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J Virol. 2012;86:3995–4008. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jackwood MW, Boynton TO, Hilt DA, McKinley ET, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH, Emergence of a group 3 coronavirus through recombination. Virology. 2010;398:98–108. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Circella E, Camarda A, Martella V, Bruni G, Lavazza A, Buonavoglia C. Coronavirus associated with an enteric syndrome on a quail farm. Avian Pathol. 2007;36:251–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: January 03, 2014
Page updated: January 03, 2014
Page reviewed: January 03, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.