Volume 21, Number 1—January 2015
Dispatch
Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus Infections Associated with Guinea Pigs
Figure
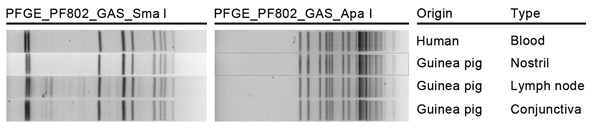
Figure. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) patterns for 4 Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus isolates from 1 person and 3 guinea pigs submitted to the Division of Consolidated Laboratory Services, Virginia, USA. Patterns indicate that all 4 isolates were indistinguishable by the SmaI and ApaI enzymes. Specimen origin and type are indicated.
Page created: December 19, 2014
Page updated: December 19, 2014
Page reviewed: December 19, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.