Volume 21, Number 1—January 2015
Dispatch
Characterization of a Multidrug-Resistant, Novel Bacteroides Genomospecies
Figure
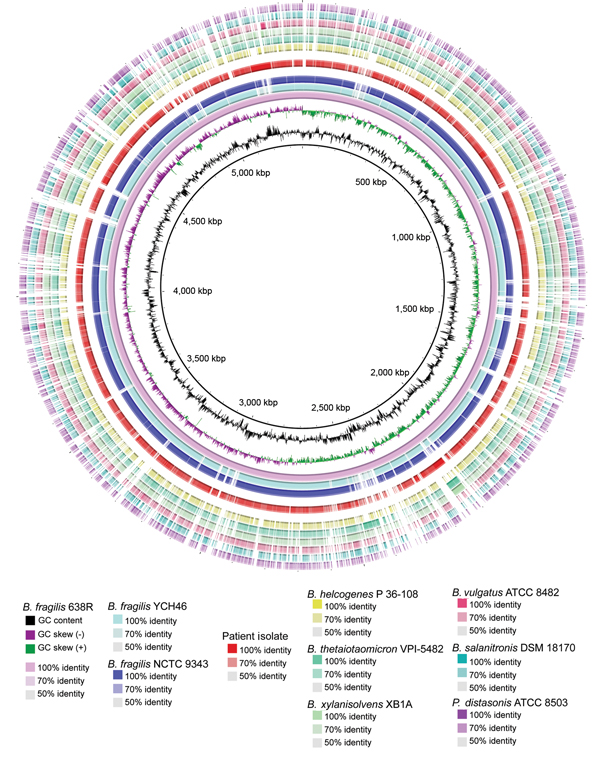
Figure. Characterization of circular plot of genome diversity between the clinical isolate of a multidrug-resistant, novel Bacteroides genomospecies and other Bacteroides spp. isolates. Reading from the center outwards, the map, GC content, and GC skew of the B. fragilis reference strain 638R are depicted. The white and colored regions of the following outer rings indicate regions absent and present, respectively, in genomes of the indicated organism compared with the genome of B. fragilis reference strain 638R. Intensity of coloration is proportional to the degree of sequence identity relative to the reference genome. The innermost 3 rings indicate the 3 B. fragilis reference genomes. The genome of the clinical isolate, separated from other rings by white space, follows. Non-fragilis Bacteroides species and a Parabacteroides species comprise the outermost rings. ATCC, American Type Culture Collection; DSM, Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen; NCTC, National Collection of Type Cultures.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.