Volume 21, Number 4—April 2015
Dispatch
Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhi, Gulf of Guinea Region, Africa
Figure 1
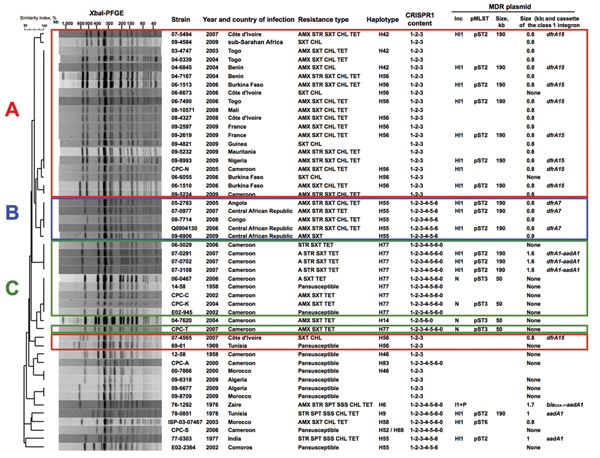
Figure 1. Characteristics of 50 Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi isolates. The dendrogram was generated by using BioNumerics version 6.6 software (Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium) and shows results of cluster analysis on the basis of XbaI–pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) fingerprinting. Similarity analysis was performed by using the Dice coefficient, and clustering analysis was performed by using UPGMA. CRISPR1, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats 1; MDR, multidrug resistant; AMX, amoxicillin; STR, streptomycin; SXT, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole; CHL, chloramphenicol; TET, tetracycline; SPT, spectinomycin; SSS, sulfamethoxazole. Zaire is the former name of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Plasmid multilocus sequence typing (pMLST) was performed as described for incN http://pubmlst.org/plasmid/) or incHI1 (4). Plasmid size was estimated by using S1 nuclease PFGE (14). For isolates from Africa, red indicates linage A, blue indicates lineage B, and green indicates lineage C.
References
- Buckle GC, Walker CL, Black RE. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever: systematic review to estimate global morbidity and mortality for 2010. J Glob Health. 2012;2:010401. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roumagnac P, Weill FX, Dolecek C, Baker S, Brisse S, Chinh NT, Evolutionary history of Salmonella Typhi. Science. 2006;314:1301–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holt KE, Parkhill J, Mazzoni CJ, Roumagnac P, Weill FX, Goodhead I, High-throughput sequencing provides insights into genome variation and evolution in Salmonella Typhi. Nat Genet. 2008;40:987–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Phan MD, Kidgell C, Nair S, Holt KE, Turner AK, Hinds J, Variation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi IncHI1 plasmids during the global spread of resistant typhoid fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:716–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Holt KE, Phan MD, Baker S, Duy PT, Nga TV, Nair S, Emergence of a globally dominant IncHI1 plasmid type associated with multiple drug resistant typhoid. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5:e1245. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kariuki S, Revathi G, Kiiru J, Mengo DM, Mwituria J, Muyodi J, Typhoid in Kenya is associated with a dominant multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi haplotype that is also widespread in Southeast Asia. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:2171–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Akinyemi KO, Coker AO. Trends of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhi isolated from hospitalized patients from 1997 to 2004 in Lagos, Nigeria. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2007;25:436–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mills-Robertson F, Addy ME, Mensah P, Crupper SS. Molecular characterization of antibiotic resistance in clinical Salmonella typhi isolated in Ghana. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002;215:249–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gross U, Amuzu SK, de Ciman R, Kassimova I, Gross L, Rabsch W, Bacteremia and antimicrobial drug resistance over time, Ghana. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1879–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dagnra AY, Akolly K, Gbadoe A, Aho K, David M. Emergence of multidrug resistant Salmonella strains in Lome (Togo) [in French]. Med Mal Infect. 2007;37:266–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lunguya O, Lejon V, Phoba MF, Bertrand S, Vanhoof R, Verhaegen J, . Salmonella Typhi in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: fluoroquinolone decreased susceptibility on the rise. EPLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012; 6:e1921. Doe: . Pub 2012 Nov 5.DOIGoogle Scholar
- Cooke FJ, Day M, Wain J, Ward LR, Threlfall EJ. Cases of typhoid fever imported to England, Scotland and Wales (2000–2003). Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2007;101:398–404. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Loury P, Tillaut H, Faisant M, Paillereau N, Marquis M, Mari C, Cluster of typhoid fever cases in Ille-et-Vilaine (France), April 2009 [in French]. Bull Epidémiol Hebd. 2010;44:446–8.
- Le Hello S, Harrois D, Bouchrif B, Sontag L, Elhani D, Guibert V, Highly drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198-X1: a microbiological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:672–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fabre L, Le Hello S, Roux C, Issenhuth-Jeanjean S, Weill FX. CRISPR is an optimal target for the design of specific PCR assays for Salmonella enterica serotypes Typhi and Paratyphi A. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2671 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: University of Limoges, Limoges, France.
3Current affiliation: Rockefeller University, New York, New York, USA.
4Current affiliation: Institute Pasteur de Dakar, Dakar, Senegal.