Volume 21, Number 8—August 2015
Perspective
Drivers of Emerging Infectious Disease Events as a Framework for Digital Detection
Figure 1
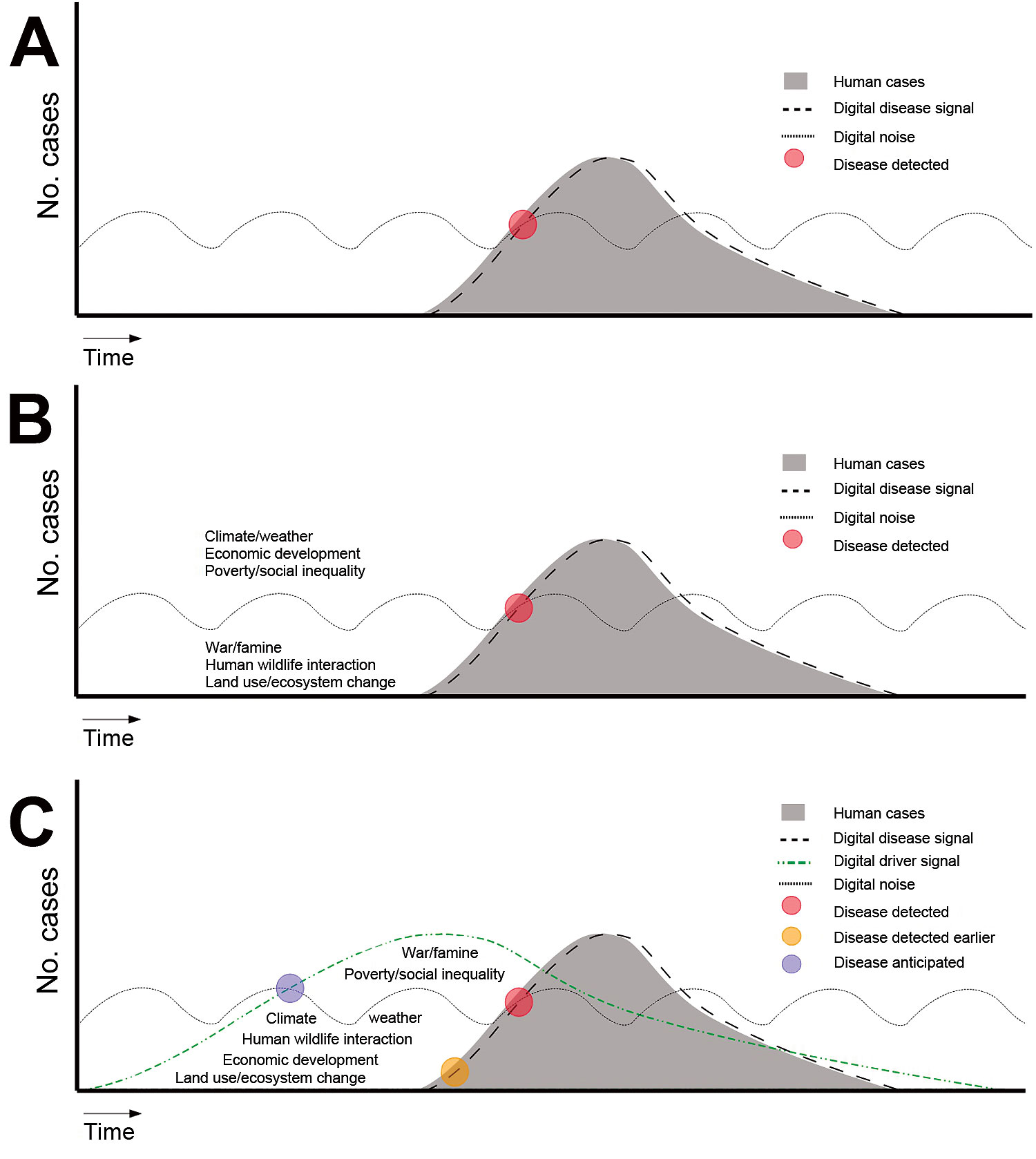
Figure 1. Surveillance and detection of disease by traditional (A, B) and digital (C) detection systems. A) Traditional disease detection, in which a close association exists between the number of cases and the digital disease signal. Disease is detected when the signal exceeds the noise. B) Disease emergence or outbreaks often occur following a driver. Examples of such drivers include climate and weather, economic development, poverty and social inequality, war and famine, human–wildlife interactions, land use and ecosystem changes. C) Detection of disease by using digital techniques. In this system, drivers of disease (not disease) are monitored, essentially to monitor for conditions suitable for disease emergence. Hypothetically, the careful surveillance of drivers that have been separated from digital noise could shorten the time to disease detection (as indicated by the orange dot).
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These authors were co-senior authors of this article.