Volume 22, Number 1—January 2016
Research
Waterborne Elizabethkingia meningoseptica in Adult Critical Care1
Figure 2
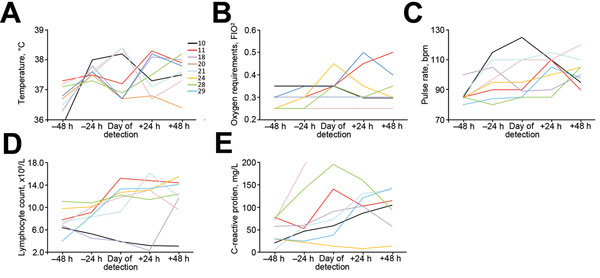
Figure 2. Clinicophysiologic parameters of patients with monomicrobial acquisition of Elizabethkingia meningoseptica in an outbreak in an adult critical care unit, London, UK, 2012–2013. Thirteen patients in the outbreak cohort were identified as having monomicrobial E. meningoseptica acquisition. Of these, 8 patients demonstrated an increase in 5 clinicophysiologic parameters of inflammation during the 48 hours before and after acquisition of E. meningoseptica: A) body temperature; B) oxygen saturation; C) pulse rate; D) lymphocyte count; and D) C-reactive protein. Patient numbers match those given in Table 1.
1Preliminary findings of this study were presented, in part, at the 27th European Society for Intensive Care Medicine conference, Barcelona, Spain, September 27– October 1, 2014.