Volume 22, Number 3—March 2016
Research
Identification of Novel Zoonotic Activity of Bartonella spp., France
Figure
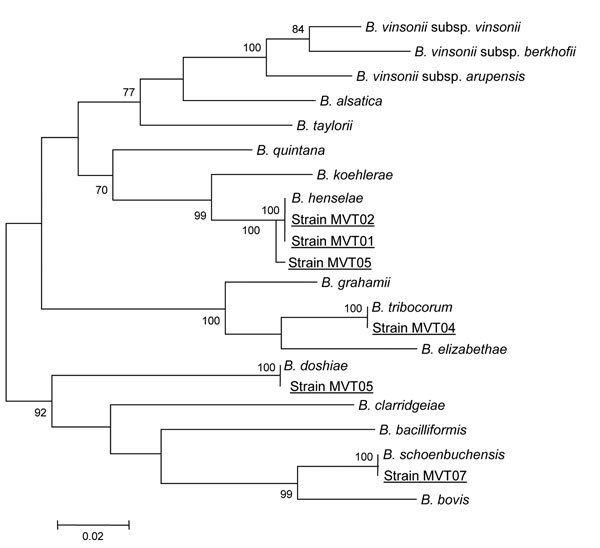
Figure. rpoB gene-based phylogenetic tree showing the relationships of 6 Bartonella isolates (underlined). Briefly, rpoB nucleotide sequences were aligned by using ClustalW software (http://www.clustal.org/clustal2/), and phylogenetic relationships were inferred by using the maximum-likelihood strategy and MEGA software (http://www.megasoftware.net). Bootstrap values above 70%, obtained from 500 analyses, are indicated at the nodes. Scale bar represents a 2% nucleotide sequence divergence.
Page created: February 18, 2016
Page updated: February 18, 2016
Page reviewed: February 18, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.