Volume 22, Number 9—September 2016
Research
Staphylococcus aureus Regulatory RNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Bloodstream Infections
Figure 4
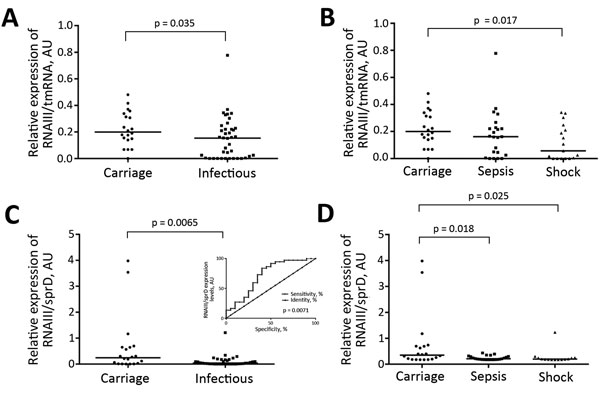
Figure 4. Discrimination of colonizing strains of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with bloodstream infections, Rennes, France. A) RNAIII analysis of strains from carriers and infected persons; B) RNAIII analysis of strains from carriers and persons with nonsevere sepsis or septic shock; C) RNAII/sprD analysis of strains from carriers and infected persons; D) RNAII/sprD analysis of strains from carriers and persons with nonsevere sepsis or septic shock. RNAIII and sprD levels were calculated relative to those for tmRNA. RNAIII expression was monitored by quantitative PCR during early exponential growth phase for 61 strains. p values (by Mann-Whitney U test) for significant differences are shown. Panel C inset shows receiver operating characteristic analysis showing discrimination of carriage strains from infectious strains. Horizontal lines indicate medians. Using the comparative cycle threshold method, we normalized the amount of RNAIII against that of tmRNA relative to that for control strain L102 (methicillin-susceptible S. aureus colonization strain). Each symbol indicates mean for 3 independent experiments. AU, arbitrary units; spr, small pathogenicity island RNA; tmRNA, transfer–messenger RNA.