Volume 23, Number 12—December 2017
Dispatch
West Nile Virus Lineage 2 in Horses and Other Animals with Neurologic Disease, South Africa, 2008–2015
Figure 2
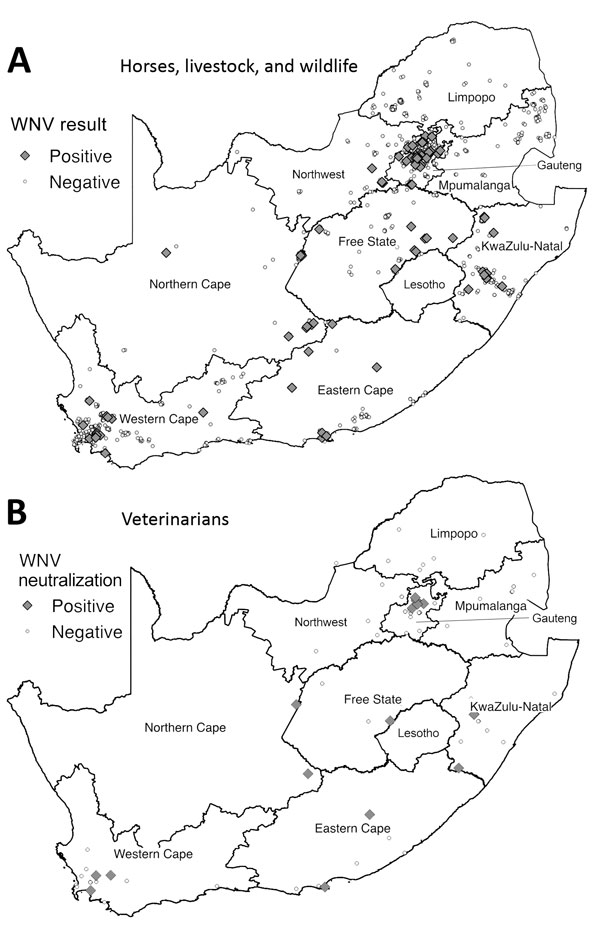
Figure 2. Distribution of WNV cases among horses, livestock animals, and wildlife species during 2008–2015 and of WNV neutralizing antibody‒positive veterinarians involved in equine, wildlife, and livestock disease management during 2011‒2012, South Africa. A) Samples were collected from horses during 2008–2015 and from livestock and wildlife 2010–2015. Samples were considered positive if they tested positive for WNV genome by PCR or for WNV IgM by WNV IgM Capture ELISA (IDEXX Laboratories, Montpellier, France) and WNV neutralizing antibody by neutralization assay. B) Distribution of veterinarians described in previous report (11). Human serum was considered positive if virus neutralization was observed at a titer of 1:10 and higher. WNV, West Nile virus.
References
- Jupp PG. The ecology of West Nile virus in South Africa and the occurrence of outbreaks in humans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;951:143–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Petersen LR, Roehrig JT. West Nile virus: a reemerging global pathogen. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7:611–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Danis K, Papa A, Theocharopoulos G, Dougas G, Athanasiou M, Detsis M, et al. Outbreak of West Nile virus infection in Greece, 2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1868–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ward MP, Schuermann JA, Highfield LD, Murray KO. Characteristics of an outbreak of West Nile virus encephalomyelitis in a previously uninfected population of horses. Vet Microbiol. 2006;118:255–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ward MP, Scheurmann JA. The relationship between equine and human West Nile virus disease occurrence. Vet Microbiol. 2008;129:378–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burt FJ, Grobbelaar AA, Leman PA, Anthony FS, Gibson GV, Swanepoel R. Phylogenetic relationships of southern African West Nile virus isolates. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:820–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zaayman D, Venter M. West Nile virus neurologic disease in humans, South Africa, September 2008-may 2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:2051–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Venter M, Human S, Zaayman D, Gerdes GH, Williams J, Steyl J, et al. Lineage 2 west nile virus as cause of fatal neurologic disease in horses, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:877–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bakonyi T, Ivanics E, Erdélyi K, Ursu K, Ferenczi E, Weissenböck H, et al. Lineage 1 and 2 strains of encephalitic West Nile virus, central Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:618–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ward MP, Levy M, Thacker HL, Ash M, Norman SK, Moore GE, et al. Investigation of an outbreak of encephalomyelitis caused by West Nile virus in 136 horses. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004;225:84–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Eeden C, Swanepoel R, Venter M. Antibodies against West Nile and Shuni viruses in veterinarians, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1409–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Niekerk S, Human S, Williams J, van Wilpe E, Pretorius M, Swanepoel R, et al. Sindbis and Middelburg old world alphaviruses associated with neurologic disease in horses, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:2225–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guthrie AJ, Maclachlan NJ, Joone C, Lourens CW, Weyer CT, Quan M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a duplex real-time reverse transcription quantitative PCR assay for detection of African horse sickness virus. J Virol Methods. 2013;189:30–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Venter M, Human S, van Niekerk S, Williams J, van Eeden C, Freeman F. Fatal neurologic disease and abortion in mare infected with lineage 1 West Nile virus, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1534–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Venter M, Steyl J, Human S, Weyer J, Zaayman D, Blumberg L, et al. Transmission of West Nile virus during horse autopsy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010;16:573–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar