Volume 23, Number 2—February 2017
Synopsis
Changing Epidemiology of Human Brucellosis, China, 1955–2014
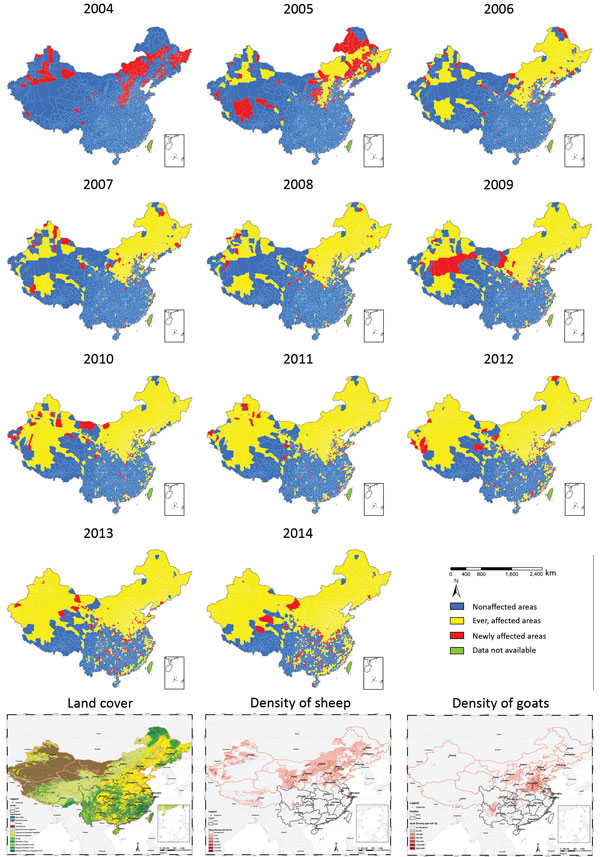
Figure 6
References
- Franco MP, Mulder M, Gilman RH, Smits HL. Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:775–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, Christou L, Tsianos EV. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:91–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E. Brucellosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2325–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dean AS, Crump L, Greter H, Schelling E, Zinsstag J. Global burden of human brucellosis: a systematic review of disease frequency. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:e1865. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rubach MP, Halliday JE, Cleaveland S, Crump JA. Brucellosis in low-income and middle-income countries. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2013;26:404–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dean AS, Crump L, Greter H, Hattendorf J, Schelling E, Zinsstag J. Clinical manifestations of human brucellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:e1929. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greenfield RA, Drevets DA, Machado LJ, Voskuhl GW, Cornea P, Bronze MS. Bacterial pathogens as biological weapons and agents of bioterrorism. Am J Med Sci. 2002;323:299–315. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boone HW. Malta fever in China. China Medical Missionary Journal. 1905;19:167–73.
- Chungking Men’s Hospital Report, 1905. China Medical Missionary Journal. 1906;20:187–8.
- Maxwell JR. Undulant and paratyphoid fevers in Fukien Province. Chin Med J (Engl). 1916;30:100–3.
- Lim CE. Isolation of M. melitensis from patients in China. Far Eastern Association of Tropical Medicine Transactions. Sixth Biennial Congress, Tokyo. 1925;2:763–4.
- Tung T, Zia SH. Undulant fever among laboratory workers. Chinese Medical Journal. 1936;50:1203–10.
- Zia SH, Wang FL. Brucellosis in north China; a clinical, etiological and epidemiological study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1949;29:925–36.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deqiu S, Donglou X, Jiming Y. Epidemiology and control of brucellosis in China. Vet Microbiol. 2002;90:165–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shang D. [Progress in the study of prevention and control of Brucellosis in China in last 50 years] [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2000;21:55–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gang S, Zhao Y, Zhang S. Analysis of 1990 to 2001 surveillance effect of national major surveillance place for brucellosis [in Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases. 2002;17:285–8.
- Jia P, Joyner A. Human brucellosis occurrences in inner mongolia, China: a spatio-temporal distribution and ecological niche modeling approach. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li Y, Yu X, Wang D, Li T. Characteristics of brucellosis related public health emergencies in China, 2006–2012 [in Chinese]. Dis Surveill. 2013;28:723–5.
- Tan Z, Huang Y, Liu G, Zhou W, Xu X, Zhang Z, et al. A familial cluster of human brucellosis attributable to contact with imported infected goats in Shuyang, Jiangsu Province, China, 2013. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93:757–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen S, Zhang H, Liu X, Wang W, Hou S, Li T, et al. Increasing threat of brucellosis to low-risk persons in urban settings, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:126–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen Z, Zhang W, Ke Y, Wang Y, Tian B, Wang D, et al. High-risk regions of human brucellosis in china: implications for prevention and early diagnosis of travel-related infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:330–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhang J, Yin F, Zhang T, Yang C, Zhang X, Feng Z, et al. Spatial analysis on human brucellosis incidence in mainland China: 2004-2010. BMJ Open. 2014;4:e004470. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li YJ, Li XL, Liang S, Fang LQ, Cao WC. Epidemiological features and risk factors associated with the spatial and temporal distribution of human brucellosis in China. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:547. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang L, Wang Y, Jin S, Wu Z, Chin DP, Koplan JP, et al. Emergence and control of infectious diseases in China. Lancet. 2008;372:1598–605. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- General Office of the State Council. People’s Republic of China. National mid-term and long-term animal disease control plan of China, 2012–2020 [cited 2015 Aug 27]. http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2012-05/25/content_2145581.htm
- Feng L, Shay DK, Jiang Y, Zhou H, Chen X, Zheng Y, et al. Influenza-associated mortality in temperate and subtropical Chinese cities, 2003-2008. Bull World Health Organ. 2012;90:279–288B. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chatfield C, Yar M. Holt-Winters forecasting: some practical issues. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series D (The Statistician). Special Issue: Statistical Forecasting and Decision-Making. 1988;37:129–40.
- Tuanmu M, Jetz W. A global 1-km consensus land-cover product for biodiversity and ecosystem modelling. Glob Ecol Biogeogr. 2014;23:1031–45. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Robinson TP, Wint GR, Conchedda G, Van Boeckel TP, Ercoli V, Palamara E, et al. Mapping the global distribution of livestock. PLoS One. 2014;9:e96084. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Bank. Urban population and GDP per capita of China [cited 2015 Sep 15]. http://data.worldbank.org/country/china
- Zhang S, Zhu D, Gang S. A review of brucellosis control and prevention in the last 50 years in China [in Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases. 2003;18:275–8.
- Man T, Wang D, Cui B, Wang Y, Ding F, Li T, et al. Analysis on surveillance data of brucellosis in China, 2009 [in Chinese]. Dis Surv. 2010;25:944–6.
- Wang D, Li T, Gang S, Zhao Y, Liu F, Wang J. Analysis on surveillance data of brucellosis in China, 2007 [in Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases. 2008;23:443–5.
- Zhao Y, Wang D, Gang S. Report of brucellosis surveillance in China, 2005–2006 [in Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases. 2008;23:38–40.
- Zhao Y, Wang D, Gang S. Analysis on the surveillance results of the national main monitoring station of the brucellosis in 2001 to 2004 [in Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases. 2005;20:247–9.
- Zhan D, Ruan S, Gongsang Q, Cui B. Epidemiological analysis of brucellosis in Nagqu and Qamdo, Tibet in 2006 [in Chinese]. Dis Surv. 2008;23:285–6.
- Zinsstag J, Schelling E, Waltner-Toews D, Whittaker M, Tanner M, editors. One Health: the theory and practice of integrated health approaches. Oxfordshire (UK): CABI; 2015.
- National Development and Reform Commission of China. National beef and mutton production development plan (2013–2020) [cited 2015 Aug 28]. http://www.sdpc.gov.cn/zcfb/zcfbghwb/201402/P020140221362074574291.pdf
- Chen JD, Ke CW, Deng X, Jiang S, Liang W, Ke BX, et al. Brucellosis in Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China, 2005-2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:817–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alirol E, Getaz L, Stoll B, Chappuis F, Loutan L. Urbanisation and infectious diseases in a globalised world. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:131–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goodwin ZI, Pascual DW. Brucellosis vaccines for livestock. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016;181:51–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen Y, Ke Y, Wang Y, Yuan X, Zhou X, Jiang H, et al. Changes of predominant species/biovars and sequence types of Brucella isolates, Inner Mongolia, China. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:514. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bonfoh B, Kasymbekov J, Dürr S, Toktobaev N, Doherr MG, Schueth T, et al. Representative seroprevalences of brucellosis in humans and livestock in Kyrgyzstan. EcoHealth. 2012;9:132–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tatem AJ. Mapping population and pathogen movements. Int Health. 2014;6:5–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kasymbekov J, Imanseitov J, Ballif M, Schürch N, Paniga S, Pilo P, et al. Molecular epidemiology and antibiotic susceptibility of livestock Brucella melitensis isolates from Naryn Oblast, Kyrgyzstan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2047. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roth F, Zinsstag J, Orkhon D, Chimed-Ochir G, Hutton G, Cosivi O, et al. Human health benefits from livestock vaccination for brucellosis: case study. Bull World Health Organ. 2003;81:867–76.PubMedGoogle Scholar
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: January 17, 2017
Page updated: January 17, 2017
Page reviewed: January 17, 2017
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.