Volume 23, Number 2—February 2017
Research
Detection of Multiple Parallel Transmission Outbreak of Streptococcus suis Human Infection by Use of Genome Epidemiology, China, 2005
Figure 1
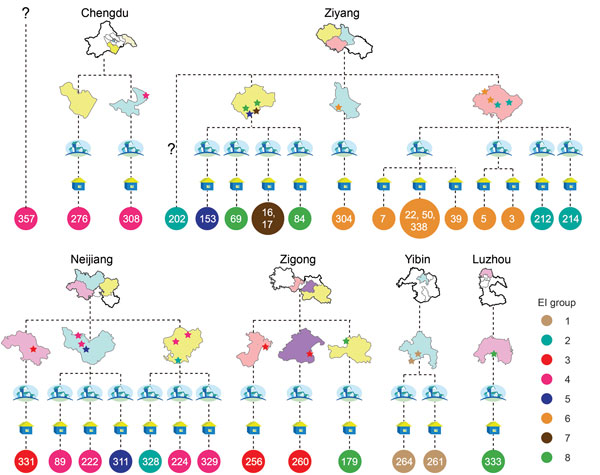
Figure 1. Geographic locations of resident villages of persons infected during outbreak of Streptococcus suis identified by whole-genome sequencing as minimum core genome type 1 sequence type 7, Sichuan Province, China, 2005. The 4 levels of administrative divisions (city, county, town, and village) are displayed to show the geographic locations and relationships of isolates. Drawings of the cities and counties are simplified maps of those territories. Towns are depicted with 4 houses, and villages are depicted with 1 house. Stars indicate the locations of patients infected by isolates of the 8 epidemiologically interesting groups, and isolates in the same group are shown in the same color. Circles with numbers represent the isolates, and colors are consistent with the color of the stars. Locations of some isolates were too close to distinguish them on the map (e.g., SC7, SC22, SC50, SC338, and SC39). EI, epidemiologically interesting.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.