Volume 23, Number 2—February 2017
Research
Detection of Multiple Parallel Transmission Outbreak of Streptococcus suis Human Infection by Use of Genome Epidemiology, China, 2005
Figure 3
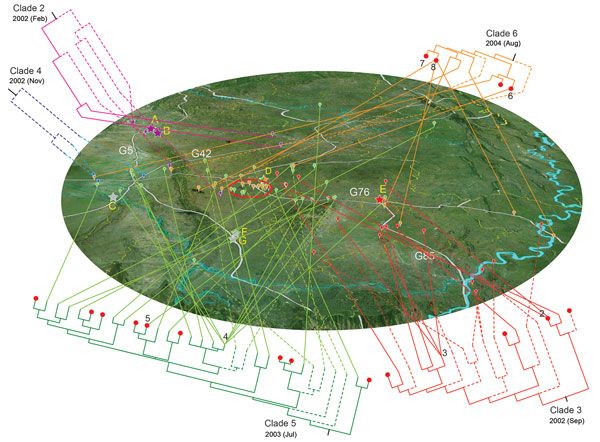
Figure 3. Geographic spread of the 5 outbreak clades of Streptococcus suis minimum core genome type 1 sequence type 7 before and during outbreak of S. suis human infections, Sichuan Province, China, 2005. Phylogenetic relationship of isolates within a clade is detailed in Technical Appendix 2 Figure 1). Lineages that developed before 2005 are marked with dashed lines. Clades are displayed separately around the map for better visualization of their geographic distribution. Locations are marked by bubbles in different colors (clades 2–6 are purple, red, blue, green, and orange respectively). The isolates in the same epidemiologically interesting group are collapsed at the tip of the tree and identified by their group number. Bubbles in the red ellipse on the map represent isolates from the most concentrated outbreak region of Ziyang city; red plots on the tree represent these isolates; stars represent the piglet breeding companies.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.