Volume 23, Number 2—February 2017
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Multidrug-Resistant Candida haemulonii and C. auris, Tel Aviv, Israel
Figure 4
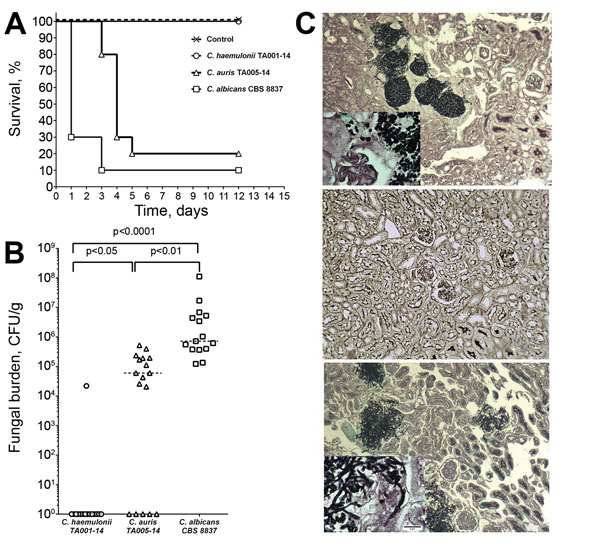
Figure 4. Differing virulence of Candida auris and C. haemulonii assessed in a mouse model of hematogenous disseminated candidiasis. Virulence was assessed in immunosuppressed BALB/c mice after intravenous injection of yeast cell suspension. A) Survival curves showing significantly shorter survival of mice infected with C. albicans than C. auris and no death among mice infected with C. haemulonii. B) Kidney fungal load (CFU per gram of tissue) shown to be significantly higher in mice infected with C. albicans than in those infected with C. auris, whereas no viable yeast was cultured from kidneys of mice infected with C. haemulonii. C) In mouse kidneys, C. auris cells formed aggregates and no hyphae (top) whereas C. albicans formed extensive tissue-invasive hyphae (bottom); C. haemulonii was not detected in tissue sections (middle). Grocott methenamine silver staining, original magnification ×100 for panels, ×400 for insets.