Volume 23, Number 5—May 2017
Dispatch
Virulence Analysis of Bacillus cereus Isolated after Death of Preterm Neonates, Nice, France, 2013
Figure 2
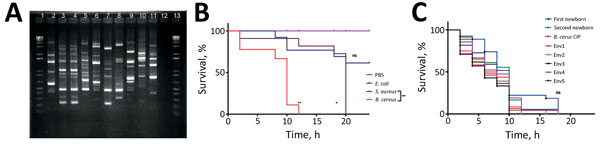
Figure 2. Genetic and virulence analyses of Bacillus spp. strains isolated from 2 preterm neonates with B. cereus infection and environmental sampling from intensive care unit, Nice, France, 2013. A) Molecular typing using M13-PCR methods, as described by Guinebretiere et al. (5). Lane 1, DNA ladder; lane 2, tracheobronchial fluid, first newborn; lane 3, blood culture, second newborn; lane 4, catheter, second newborn; lane 5, incubator surface, first newborn (Env1); lane 6, incubator surface, first newborn (Env2); lane 7, incubator surface, first newborn (Env3); lane 8, ultrasonographic probe (Env4); lane 9, bench surface used for bottle feeding (Env5); lane 10, incubator surface, second newborn (1); lane 11, incubator surface, second newborn (2); lane 12, negative control; lane 13, DNA ladder. B) Survival of flies infected with Escherichia coli CIP 102181, Staphylococcus aureus CIP 110856, and B. cereus CIP 66.24 T, compared with survival of control flies injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). *p <0.01; **p <0.001; ns, not significant (all by Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon χ2 test). C) Survival of flies infected with the different strains of B. cereus tested. Env, environmental; ns, not significant by Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon χ2 test.
References
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Risks for public health related to the presence of Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus spp. including Bacillus thuringiensis in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2016;14:4524. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Bottone EJ. Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:382–98. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Girisch M, Ries M, Zenker M, Carbon R, Rauch R, Hofbeck M. Intestinal perforations in a premature infant caused by Bacillus cereus. Infection. 2003;31:192–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hilliard NJ, Schelonka RL, Waites KB. Bacillus cereus bacteremia in a preterm neonate. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:3441–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guinebretière MH, Nguyen-The C. Sources of Bacillus cereus contamination in a pasteurized zucchini purée processing line, differentiated by two PCR-based methods. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2003;43:207–15. PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guinebretiere MH, Fagerlund A, Granum PE, Nguyen-The C. Rapid discrimination of cytK-1 and cytK-2 genes in Bacillus cereus strains by a novel duplex PCR system. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;259:74–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ehling-Schulz M, Vukov N, Schulz A, Shaheen R, Andersson M, Märtlbauer E, et al. Identification and partial characterization of the nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene responsible for cereulide production in emetic Bacillus cereus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:105–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cadot C, Tran SL, Vignaud ML, De Buyser ML, Kolstø AB, Brisabois A, et al. InhA1, NprA, and HlyII as candidates for markers to differentiate pathogenic from nonpathogenic Bacillus cereus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48:1358–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guinebretière MH, Thompson FL, Sorokin A, Normand P, Dawyndt P, Ehling-Schulz M, et al. Ecological diversification in the Bacillus cereus Group. Environ Microbiol. 2008;10:851–65. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boyer L, Magoc L, Dejardin S, Cappillino M, Paquette N, Hinault C, et al. Pathogen-derived effectors trigger protective immunity via activation of the Rac2 enzyme and the IMD or Rip kinase signaling pathway. Immunity. 2011;35:536–49. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ramarao N, Belotti L, Deboscker S, Ennahar-Vuillemin M, de Launay J, Lavigne T, et al. Two unrelated episodes of Bacillus cereus bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit. Am J Infect Control. 2014;42:694–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Turabelidze G, Gee JE, Hoffmaster AR, Manian F, Butler C, Byrd D, et al. Contaminated ventilator airflow sensor linked to Bacillus cereus colonization of newborns. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;5:781–3.
- Decousser JW, Ramarao N, Duport C, Dorval M, Bourgeois-Nicolaos N, Guinebretière MH, et al. Bacillus cereus and severe intestinal infections in preterm neonates: Putative role of pooled breast milk. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41:918–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar