Volume 23, Number 7—July 2017
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Clonal Clusters and Virulence Factors of Group C and G Streptococcus Causing Severe Infections, Manitoba, Canada, 2012–2014
Figure 1
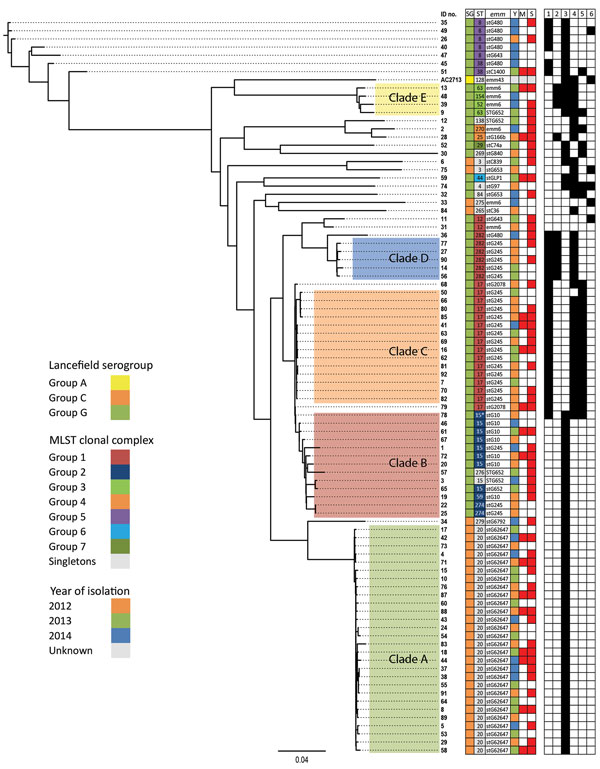
Figure 1. Maximum-likelihood whole-genome, core single-nucleotide variation (SNV) phylogenetic tree of 89 Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis isolates from the blood of patients with group C and G Streptococcus causing severe infections, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, 2012–2014. Multilocus sequence typing clonal complex relatedness groups were determined by using goeBURST (global optimal eBurst; http://www.phyloviz.net). In the mortality column, red and white squares indicate patient death and survival, respectively. In the severity column, red and white squares represent manifestation of severe and nonsevere disease, respectively. Black and white squares indicate the presence and absence of virulence factor genes, respectively. Scale bar indicates estimated evolutionary divergence between isolates, based on the average genetic distance between strains (estimated substitutions in sample/total high-quality SNVs). ICU, intensive care unit; IE, infectious endocarditis; MLST, multilocus sequence type; STSS, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome; SG, serogroup; ST, MLST; Y, year; M, mortality; S, severity; 1, cbp; 2, fbp; 3, speG; 4, sicG; 5, gfbA; 6, bca.