Volume 23, Number 7—July 2017
CME ACTIVITY - Research
Clonal Clusters and Virulence Factors of Group C and G Streptococcus Causing Severe Infections, Manitoba, Canada, 2012–2014
Figure 2
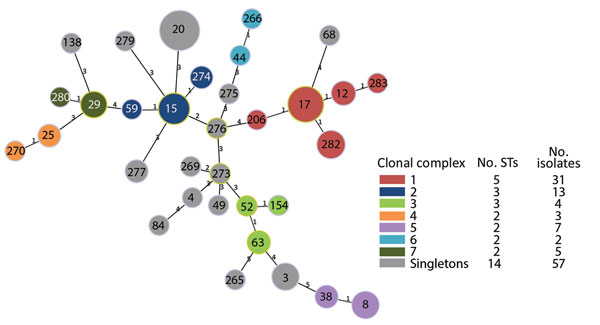
Figure 2. Minimum spanning tree representing the genetic relatedness of multilocus sequence types (MLSTs) of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis isolates from patients with group C and G Streptococcus causing severe infections, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada, 2012–2014. Genetic relatedness was determined by full goeBURST (global optimal eBurst; http://www.phyloviz.net) analysis using Streptococcus dysgalactiae MLST allelic profiles of 7 housekeeping genes. Numbers on nodes correspond to individual sequence types (STs) and colored nodes correspond to clonal cluster relatedness groups defined by a single-locus variation from a founding ST. Number labels on branches indicate the number of allelic variations between STs; branch lengths are not to scale.