Volume 23, Number 8—August 2017
Dispatch
Influenza D Virus in Animal Species in Guangdong Province, Southern China
Figure 2
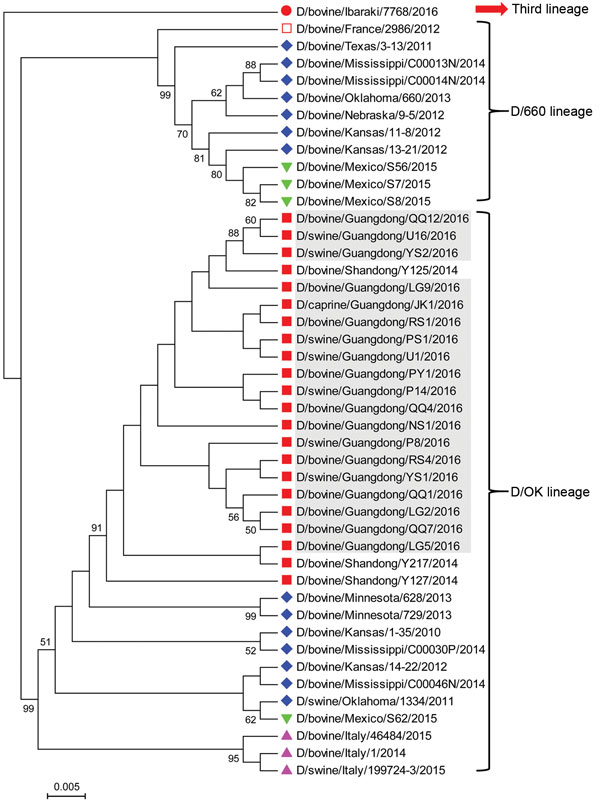
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of viruses from study of influenza D viruses in cattle, goats, buffalo, and pigs in Guangdong Province and neighboring provinces, China, compared with reference viruses. Partial hemagglutinin-esterase-fusion gene sequences (496 bp) were aligned by using ClustalW implemented in DNAStar software (DNAStar, Madison, WI, USA), and the phylogenetic tree was obtained using neighbor-joining method within MEGA 5.1 software (http://www.megasoftware.net). Numbers at nodes are percentages of bootstrap values obtained by repeated analyses (1,000 times) to generate majority consensus tree. Only bootstrap scores of at least 50 were retained. Scale bar indicates 0.5% nucleotide sequence divergence. Gray shading indicates viruses from this study; reference viruses obtained from the United States are marked with ♦; from China, ■; from Italy, ▲; from Mexico, ▼; from France, □; and from Japan ●. Note that D/swine/Guangdong/YS1/2016 and D/swine/Guangdong/YS2/2016 are from the same farm; D/swine/Guangdong/P8/2016 and D/swine/Guangdong/P14/2016 are from the same farm; D/swine/Guangdong/U1/2016 and D/swine/Guangdong/U16/2016 are from the same farm; D/bovine/Guangdong/LG2/2016, D/bovine/Guangdong/LG5/2016 and D/bovine/Guangdong/LG9/2016 are from the same farm; D/bovine/Guangdong/QQ1/2016, D/bovine/Guangdong/QQ4/2016, D/bovine/Guangdong/QQ7/2016 and D/bovine/Guangdong/QQ12/2016 are from the same farm; D/bovine/Guangdong/RS1/2016 and D/bovine/Guangdong/RS4/2016 are from the same farm.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.