Volume 23, Number 9—September 2017
Research
Convergence of Humans, Bats, Trees, and Culture in Nipah Virus Transmission, Bangladesh
Figure 2
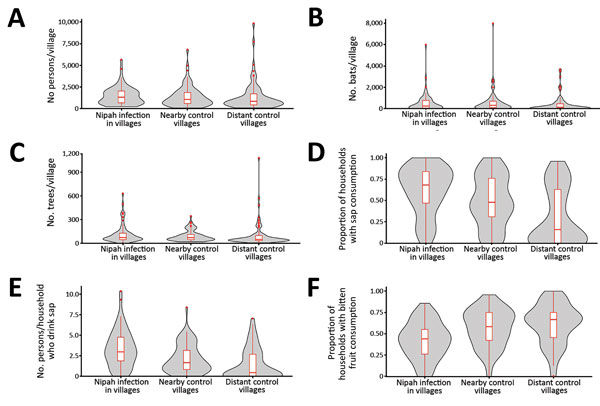
Figure 2. Comparisons of villages with Nipah virus infections with nearby and distant control villages, Bangladesh, 2011–2013. A) Human population size, B) Pteropus medius bat population size, C) no. date palm trees, D) proportion of households with members who consume fresh date palm sap, E) average no. of persons per household who consume fresh date palm sap, and F) proportion of households that reported their residents eat bitten fruits dropped on the ground. Gray shading in violin plots indicates distribution of values for each variable. Box plots indicate 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top lines), medians (horizontal lines within boxes), and 95 CIs (whiskers). Red dots indicate maximum (outlier) values.
1Current affiliation: Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA.
2Current affiliation: University of Michigan School of Public Health, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA.
3Current affiliation: Medical Research Council, Banjul, The Gambia.
4Current affiliation: University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, USA.