Volume 24, Number 3—March 2018
Research
Increasing Prevalence of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria in Respiratory Specimens from US-Affiliated Pacific Island Jurisdictions1
Figure
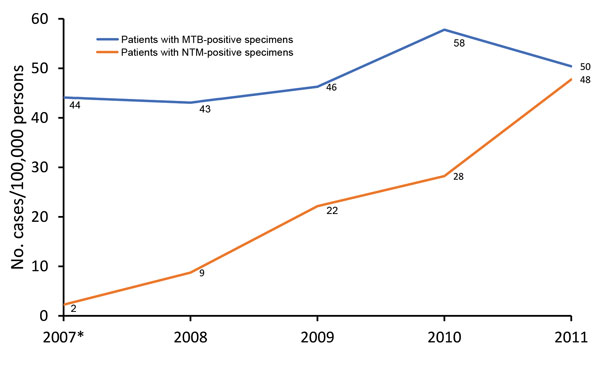
Figure. Prevalence of positive test results for NTM and MTB in respiratory specimens from patients in US-affiliated Pacific Island jurisdictions, 2007–2011. *Data for 2007 were extrapolated from data for August–December 2007. MTB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; NTM, nontuberculous mycobacteria.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the 2013 American College of Physicians Hawaii Chapter Annual Meeting, January 2, 2013, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA.
2Current affiliation: Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA.
3Current affiliation: Baptist Medical Center, Jacksonville, Florida, USA
Page created: February 15, 2018
Page updated: February 15, 2018
Page reviewed: February 15, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.