Volume 24, Number 8—August 2018
Research
Novel Enterobacter Lineage as Leading Cause of Nosocomial Outbreak Involving Carbapenemase-Producing Strains
Figure 5
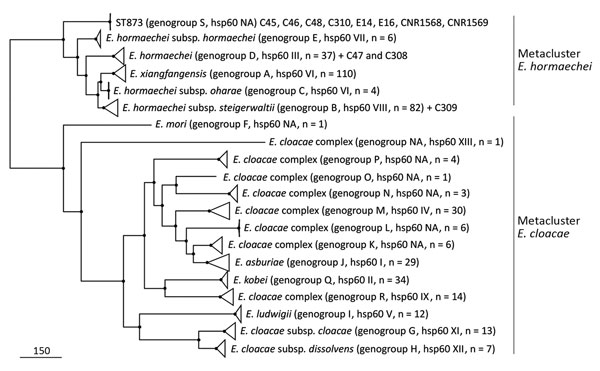
Figure 5. Approximately maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees based on recombination free core single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) inferred from ST873, ST110 and ST118 genomes and 398 representative genomes of Enterobacter cloacae complex strains in study of nosocomial outbreak involving carbapenamase-producing Enterobacter strains, Lyon, France, January 12, 2014–December 31, 2015. All nodes are supported by Shimodaira-Hasegawa test values >97%. Scale bar indicates SNPs. NA, nonattributed; ST, sequence type.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 18, 2018
Page updated: July 18, 2018
Page reviewed: July 18, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.