Volume 24, Number 8—August 2018
Dispatch
Fatal Nongroupable Neisseria meningitidis Disease in Vaccinated Patient Receiving Eculizumab
Figure 2
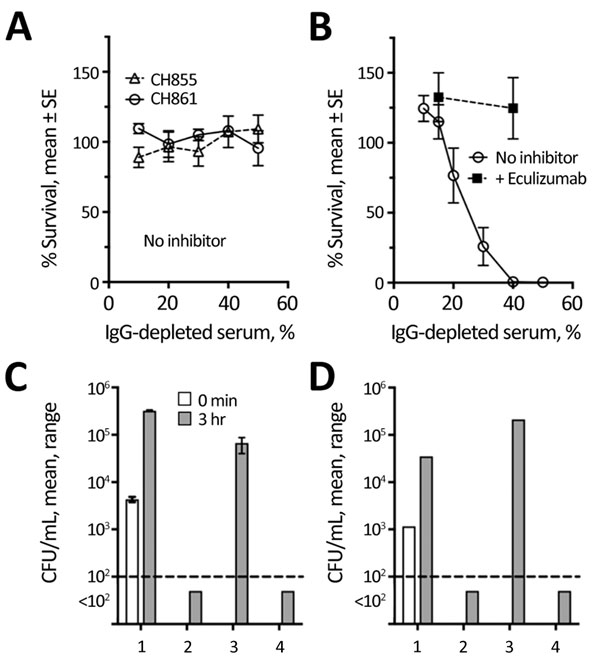
Figure 2. Effect of eculizumab on serum bactericidal activity and killing of Neisseria meningitidis by anticoagulated human blood. A) Complement-mediated bactericidal activity of an IgG-depleted human serum pool from 3 unvaccinated adult donors measured against encapsulated serogroup B strains CH855 and CH861 (data from 2–4 replicate assays for each strain). B) Bactericidal activity of pool tested in (panel A) measured against the nongroupable (NG) case isolate from a 16-year-old girl with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria who died of meningococcal disease after treatment with eculizumab (data from 5 replicate assays). The addition of 50 μg/mL of eculizumab blocked bacterial killing of the NG case-isolate (data from 3 replicates). C, D) Killing of the NG case-isolate by anticoagulated human blood from 2 healthy adults, 1 previously vaccinated with 2 doses of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B meningococcal vaccine (MenB-4C) (Bexsero; GlaxoSmithKline, Bellaria Rosia, Sovicille, Italy) with the last dose 14 months earlier (C), the other unvaccinated (D). The addition of 50 μg/mL of eculizumab to the blood from both donors blocked killing of the bacteria by the blood. The addition of a mouse anti-C7 monoclonal antibody, which blocked serum bactericidal activity (data not shown), did not inhibit whole blood killing. Similar results were obtained with blood from a third adult who had been vaccinated with MenB-4C 9 months earlier (data not shown). 1, negative control (plasma-heated at 56°C for 30 min to inactivate complement activity); 2, no inhibitor; 3, eculizumab; 4, anti-C7 (24 whole blood assay).