Volume 24, Number 9—September 2018
Research
Novel Orthopoxvirus and Lethal Disease in Cat, Italy
Figure 3
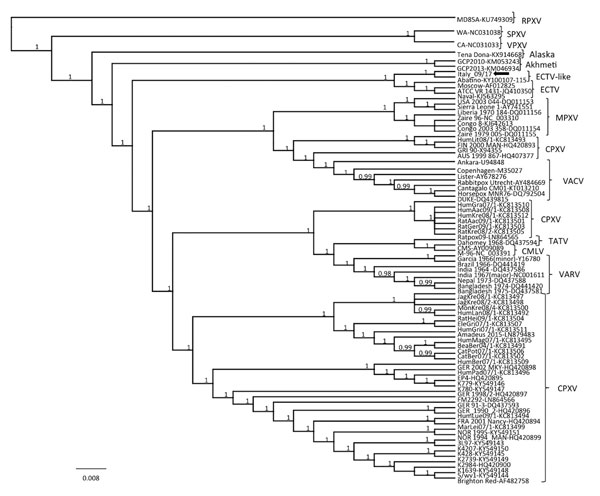
Figure 3. Phylogenetic relationship of extant orthopoxviruses with a feline poxvirus isolated from a cat, Italy. Phylogenetic tree shows 27,228 nt concatenated alignment of 9 coding gene (A7L, A10L, A24R, D1R, D5R, E6R, E9L, H4L, and J6R) sequences of orthopoxvirus. Gene designations refer to the VACV-COP genome (GenBank accession no. M35027). Posterior output of the tree was derived from Bayesian inference using 4 chains run for >1 million generations, a general time-reversible model, a proportion of invariable sites, a gamma distribution of rate variation across sites, and a subsampling frequency of 1,000. Posterior probability values >0.95 are indicated on the tree nodes. The black arrow indicates the feline poxvirus Italy_09/17 isolated in this study. Raccoonpox virus strain MD85A was used as an outgroup. Strain name, host and year of detection, location of origin, and GenBank accession numbers for orthopoxviruses used for phylogeny are shown in Table 2). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. CMLV, camelpox virus; CPXV, cowpox virus; ECTV, ectromelia virus; MPXV, monkeypox virus; RPXV, raccoonpox virus; SPXV, skunkpox virus; TATV, taterapox virus; VACV, vaccinia virus; VARV, variola virus; VPXV, volepox virus.