Volume 25, Number 1—January 2019
Dispatch
Surgical Site Infections Caused by Highly Virulent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Sequence Type 398, China
Figure 1
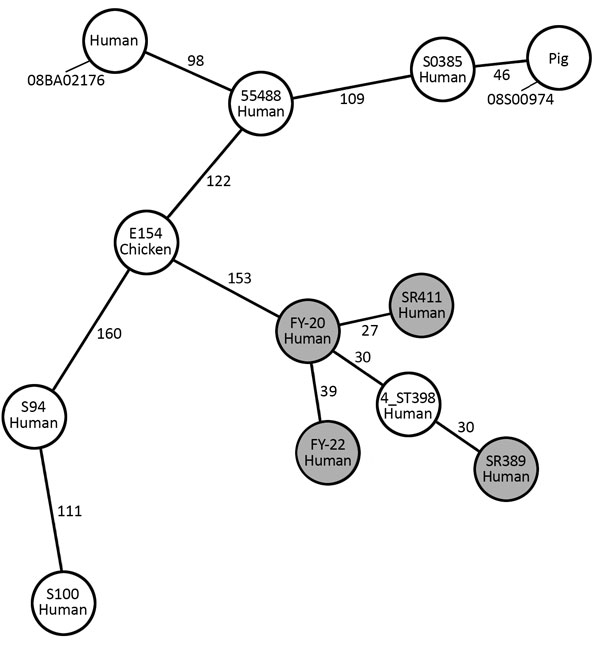
Figure 1. Minimum-spanning tree built from the core genome multilocus sequence type allelic profiles of MRSA ST398 strains from 4 patients in China (gray circles) and other ST398 strains. Each circle represents a single strain and is named with the sample and the origin. The 12 strains are based on 1,807 columns with the pairwise ignoring missing values option in Ridom SeqSphere+ software (Ridom GmbH, http://www.ridom.de/seqsphere). The numbers on the connecting lines indicate the number of allelic differences between 2 strains. S. aureus strain COL (GenBank accession no. NC_002951) is used as a reference. S0385 (human, MRSA, NC_017333.1), 08BA02176 (human, MRSA, CP003808.1), 55488 (human, MRSA, NZ_LAWV00000000), 4_ST398 (human, MRSA, He L et al, 2018), S94 (human, MSSA, AUPW00000000), S100 (human, MSSA, AUPV00000000), 08S00974 (animal, MRSA, NZ_CP020019.1), and E154 (animal, MRSA, CP013218.1) are used for comparison. MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; ST, sequence type.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.