Volume 25, Number 2—February 2019
Dispatch
Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Antibodies in Roe Deer, the Netherlands
Figure 1
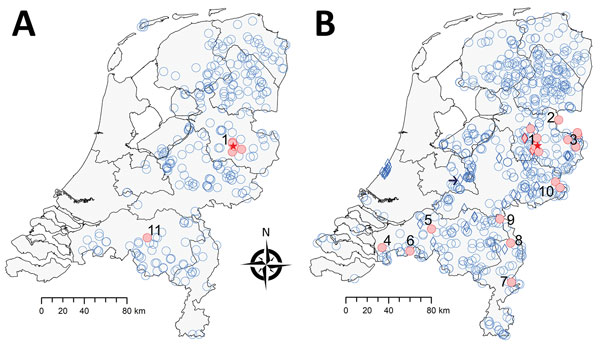
Figure 1. Geographic distribution of tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) based on serosurveillance of roe deer, the Netherlands, during A) 2010 and B) 2017. Data for 2010 were reproduced from Jahfari et al. (1). Red indicates roe deer serum samples that showed positive results in the TBEV neutralization test, and blue indicates roe deer serum samples that showed negative results in this test or an ELISA. Numbers indicate confirmed or potential foci, and red stars indicate location of 2016 TBEV-RNA positive ticks in Sallandse Heuvelrug National Park. Circles indicate sites of random sampling, and diamonds indicate sites of purposive sampling. Arrow in the right map indicates location of Utrechtse Heuvelrug National Park. Maps were constructed by using Arc-GIS software (ESRI, https://www.esri.com).
References
- Jahfari S, de Vries A, Rijks JM, Van Gucht S, Vennema H, Sprong H, et al. Tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks and roe deer, the Netherlands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:1028–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Graaf JA, Reimerink JH, Voorn GP, Bij de Vaate EA, de Vries A, Rockx B, et al. First human case of tick-borne encephalitis virus infection acquired in the Netherlands, July 2016. Euro Surveill. 2016;21:30318. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weststrate AC, Knapen D, Laverman GD, Schot B, Prick JJ, Spit SA, et al. Increasing evidence of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus transmission, the Netherlands, June 2016. Euro Surveill. 2017;22:30482. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dekker M, Laverman GD, de Vries A, Reimerink J, Geeraedts F. Emergence of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in the Netherlands. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019;10:176–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tonteri E, Kurkela S, Timonen S, Manni T, Vuorinen T, Kuusi M, et al. Surveillance of endemic foci of tick-borne encephalitis in Finland 1995-2013: evidence of emergence of new foci. Euro Surveill. 2015;20:30020. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reed LJ, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Hyg. 1938;27:493–7.
- Jahfari S, Hofhuis A, Fonville M, van der Giessen J, van Pelt W, Sprong H. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in humans with tick bites and erythema migrans, in the Netherlands. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:e0005042. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kupča AM, Essbauer S, Zoeller G, de Mendonça PG, Brey R, Rinder M, et al. Isolation and molecular characterization of a tick-borne encephalitis virus strain from a new tick-borne encephalitis focus with severe cases in Bavaria, Germany. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2010;1:44–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Donoso Mantke O, Escadafal C, Niedrig M, Pfeffer M, Working Group For Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus C. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe, 2007 to 2009. Euro Surveill. 2011;16:19976. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Seedat J. TBE: risk areas in Germany (April 2018) [in German]. Epidemiologisches Bulletin. 2018 April [cited 2018 Nov 25]. https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/EpidBull/Archiv/2018/Ausgaben/17_18.pdf?__blob=publicationFile
- Tavernier P, Sys SU, De Clercq K, De Leeuw I, Caij AB, De Baere M, et al. Serologic screening for 13 infectious agents in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) in Flanders. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2015;5:29862. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roelandt S, Suin V, Van der Stede Y, Lamoral S, Marche S, Tignon M, et al. First TBEV serological screening in Flemish wild boar. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2016;6:31099. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Valarcher JF, Hägglund S, Juremalm M, Blomqvist G, Renström L, Zohari S, et al. Tick-borne encephalitis. Rev Sci Tech. 2015;34:453–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Duscher GG, Wetscher M, Baumgartner R, Walder G. Roe deer sera used for TBE surveillance in Austria. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015;6:489–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Balling A, Plessow U, Beer M, Pfeffer M. Prevalence of antibodies against tick-borne encephalitis virus in wild game from Saxony, Germany. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014;5:805–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van der Poel WH, Van der Heide R, Bakker D, De Looff M, De Jong J, Van Manen N, et al. Attempt to detect evidence for tick-borne encephalitis virus in ticks and mammalian wildlife in The Netherlands. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005;5:58–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar