Volume 25, Number 6—June 2019
Research
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Seasonality, Beijing, China, 2007–2015
Figure 2
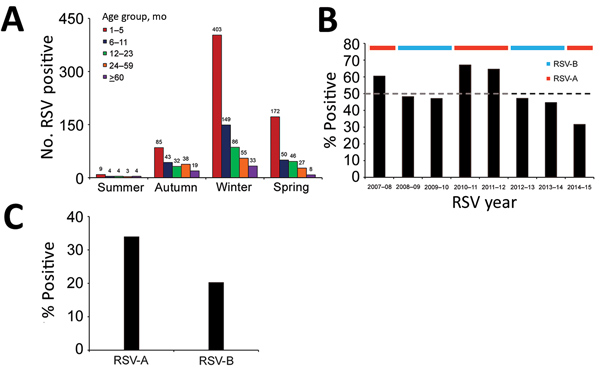
Figure 2. Hospitalized children with pneumonia testing positive for RSV, by age group, calendar season, and RSV subgroup, Beijing, China, July 1, 2007–June 30, 2015. A) Number of RSV-positive children (indicated by numbers above bars) by age group and season. Summer is defined as June–August, autumn as September–November, winter as December–February, and spring as March–May. B) Percentage of infants aged 28 days–5 months positive for RSV, by RSV season. The horizontal ribbon on top of the chart denotes the dominant RSV subgroup for that season. We assigned 2013–14 as an RSV-B–dominant season for the purposes of modeling, although the numbers of RSV-A and RSV-B cases were almost equal. Dashed line indicates 50% positivity. C) Percentage of infants 28 days–5 months of age positive for RSV, by RSV subgroup. RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; RSV-A, RSV subgroup A; RSV-B, RSV subgroup B.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.