Volume 26, Number 11—November 2020
Dispatch
Multiple Introductions of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi H58 with Reduced Fluoroquinolone Susceptibility into Chile
Figure 1
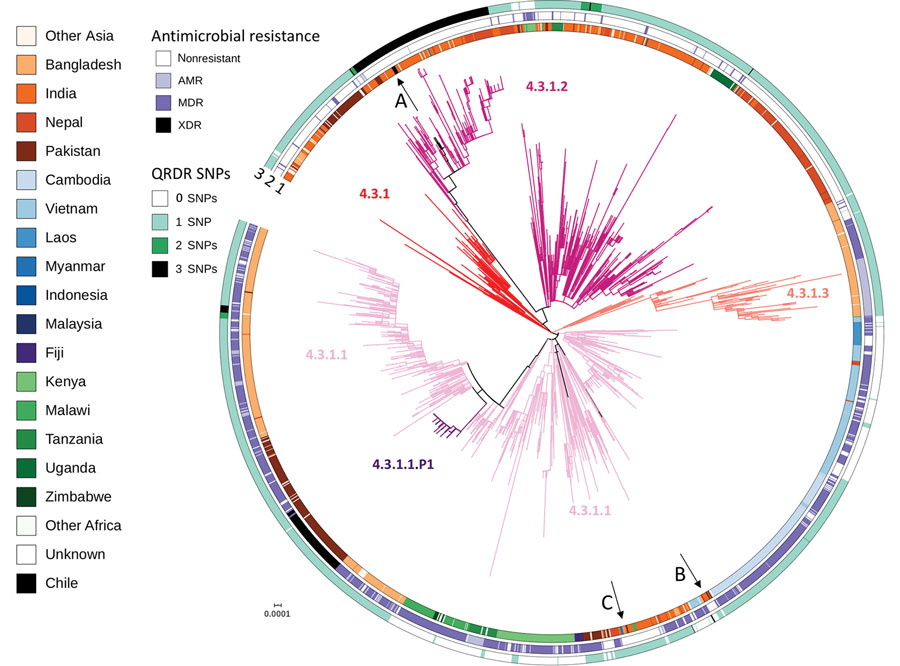
Figure 1. Global context of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi genotype 4.3.1 from Chile. Salmonella Typhi H58 genotype 4.3.1-based phylogenetic tree. Branches are colored by genotypes labeled in the tree. A, B, and C arrows indicate isolates from the Chile and the 3 independent introductions. The inner circle indicates country of isolation. The middle circle indicates AMR, excluding reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones caused by QRDR SNPs. MDR, including resistance to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; or XDR, multidrug resistance plus resistance to third-generation cephalosporins and reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones. The outer circle indicates number of SNPs, 0, 1, 2 or 3, in the quinolone resistance determining region of gyrA and parC genes. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. AMR, antimicrobial resistance; MDR, multidrug-resistant; QRDR, quinolone-resistance determining region; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; XDR, extremely drug-resistant.
1These first authors contributed equally to this work.
2These authors contributed equally to this work.