Volume 26, Number 12—December 2020
Dispatch
Circulation of 2 Barmah Forest Virus Lineages in Military Training Areas, Australia
Figure 2
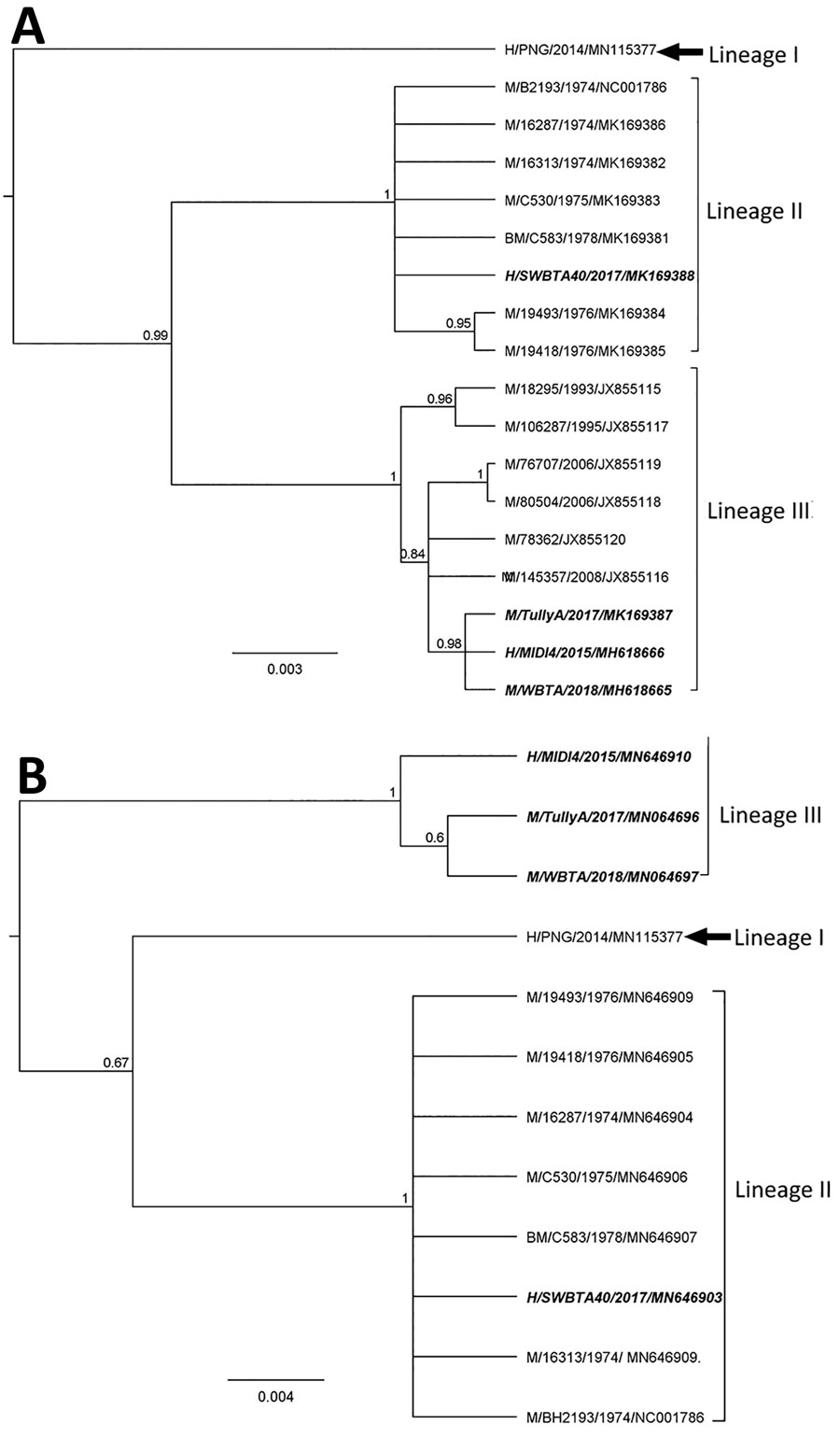
Figure 2. Phylogenies based on 17 complete BFV E2 sequences (1,263 bp) (A) and twelve 3′ untranslated region sequences (B) classify Barmah Forest virus isolates into 3 distinct lineages. We used Bayesian phylogenetic analysis method in Geneious version 11.2 (https://www.geneious.com) to analyze the aligned E2 and 3′ untranslated region sequences, applying the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano plus gamma substitution model with a gamma molecular clock model of uniform branch lengths, a chain length of 1 million, and a 10% burn-in length. The naming convention of the strains is name of host/strain/year of isolation/GenBank accession number. Scale bar indicates the length of the branches of each tree. H, humans; M, mosquitoes; BM, biting midges.
Page created: October 20, 2020
Page updated: November 19, 2020
Page reviewed: November 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.