Outbreaks of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H5N6) Virus Subclade 2.3.4.4h in Swans, Xinjiang, Western China, 2020
Yanbing Li, Minghui Li, Yulei Li, Jingman Tian, Xiaoli Bai, Cen Yang, Jianzhong Shi, Ridengcaicike Ai, Weidong Chen, Wentao Zhang, Jie Li, Yufei Kong, Yuntao Guan, and Hualan Chen

Author affiliations: State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Biotechnology, Harbin Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China (Y. Li, M. Li, Y. Li, J. Tian, X. Bai, J. Shi, C. Yang, Y. Kong, Y. Guan, H. Chen); Preventive and Control Center for Animal Disease of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Urumqi, Xinjiang Wei Autonomous Region, China (R. Ai, J. Li); Preventive and Control Center for Animal Disease of Xinjiang Crops, Urumqi (W. Zhang, J. Li)
Main Article
Figure 2
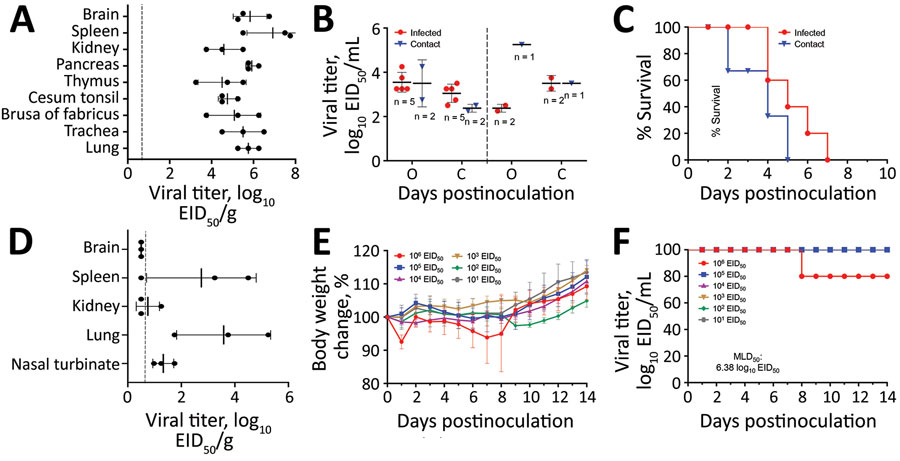
Figure 2. Replication and virulence of the WS/XJ/1/2020(H5N6) isolate in ducks and mice in a laboratory test performed after H5N6 avian influenza (H5N6) outbreaks among migratory whooper swans (Cygnus cygnus), Xinjiang Province, China, January 2020. A) Viral titer in organs of ducks that were euthanized on day 3 postinoculation. B) Viral titers in oropharyngeal and cloacal swabs from all surviving ducks were collected on days 3 and 5 postinoculation. C) Lethality of the virus in ducks. D) Viral titer in organs of mice that were euthanized on day 3 postinoculation. E) Bodyweight change of mice after inoculation with different doses of the virus. F) MLD50 of the virus. Viral titers in panels A, B, and D are shown as the mean + SD. The dashed lines indicate the lower limit of detection. EID50, 50% egg infective dose; MLD50, 50% mouse lethal dose.
Main Article
Page created: September 02, 2020
Page updated: November 19, 2020
Page reviewed: November 19, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
