Volume 26, Number 3—March 2020
Research
Acquisition of Plasmid with Carbapenem-Resistance Gene blaKPC2 in Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, Singapore
Figure 4
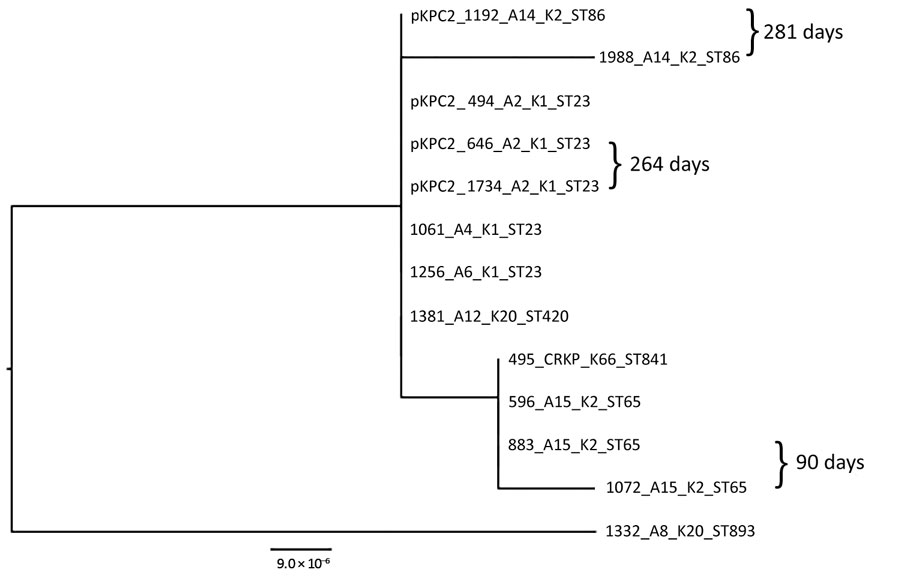
Figure 4. Maximum-likelihood analysis of pKPC2 plasmids from carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates, Singapore, 2013–2015. pKPC2_494 was used as reference. Labels indicate isolate no._patient no._K serotype_sequence type. Days between isolate collection are indicated. Scale bar indicates nucleotide changes per base pair. KPC, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase; ST, sequence type.
Page created: February 20, 2020
Page updated: February 20, 2020
Page reviewed: February 20, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.