Volume 26, Number 3—March 2020
Research
Acquisition of Plasmid with Carbapenem-Resistance Gene blaKPC2 in Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae, Singapore
Figure 6
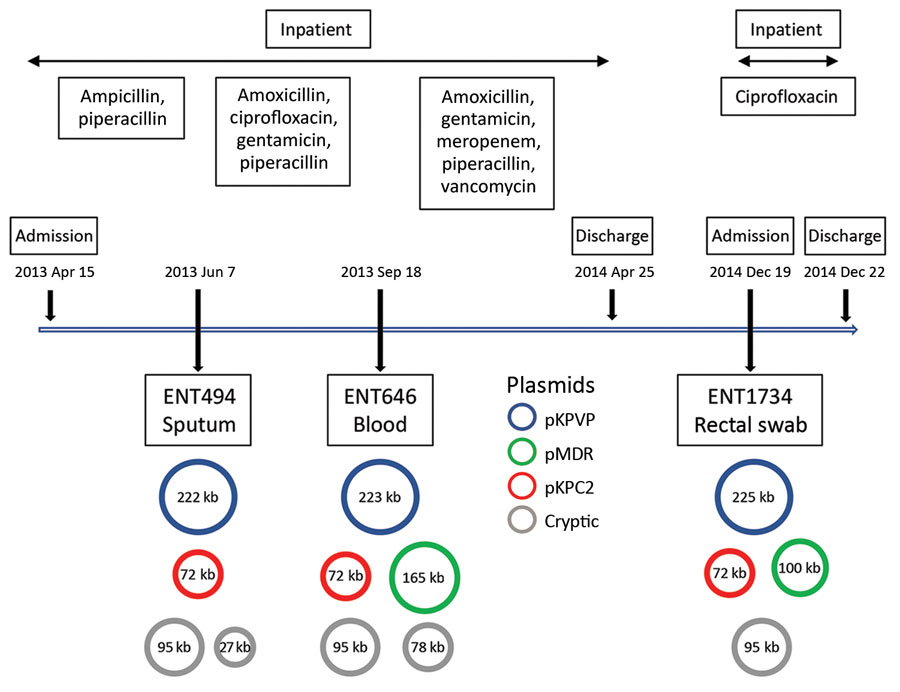
Figure 6. Timeline showing antimicrobial drug exposure and plasmid changes in 3 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from patient A2, Singapore, 2013–2014. pMDR646 contains genes aac(6’)-lb-cr,blaOXA-1, qnrB1, catB3, and dfrA14. pMDR1734 contains genes aac(6’)-lb-cr, blaOXA-1, and catB3. pKPC2 contains genes blaKPC-2, blaTEM-1A, blaTEM-1B, and mph(A). KPC, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase; KPVP, Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence plasmid; MDR, multidrug resistance.
Page created: February 20, 2020
Page updated: February 20, 2020
Page reviewed: February 20, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.