Volume 26, Number 5—May 2020
Dispatch
Pretreatment Out-of-Pocket Expenses for Presumptive Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients, India, 2016–2017
Figure 2
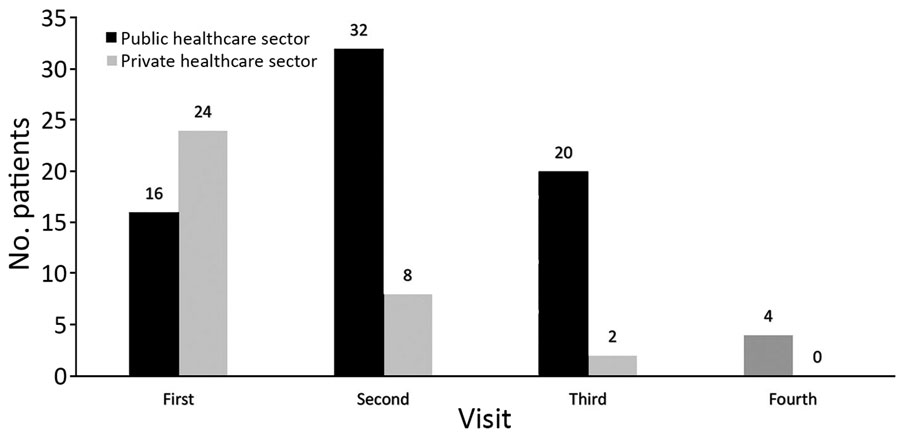
Figure 2. Distribution of visits to healthcare facilities in the public and private sectors by 40 presumptive multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients before seeking care through programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis, India, 2016–2017.
Page created: April 16, 2020
Page updated: April 16, 2020
Page reviewed: April 16, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.