Volume 26, Number 6—June 2020
Research
Endemic Chromoblastomycosis Caused Predominantly by Fonsecaea nubica, Madagascar1
Figure 3
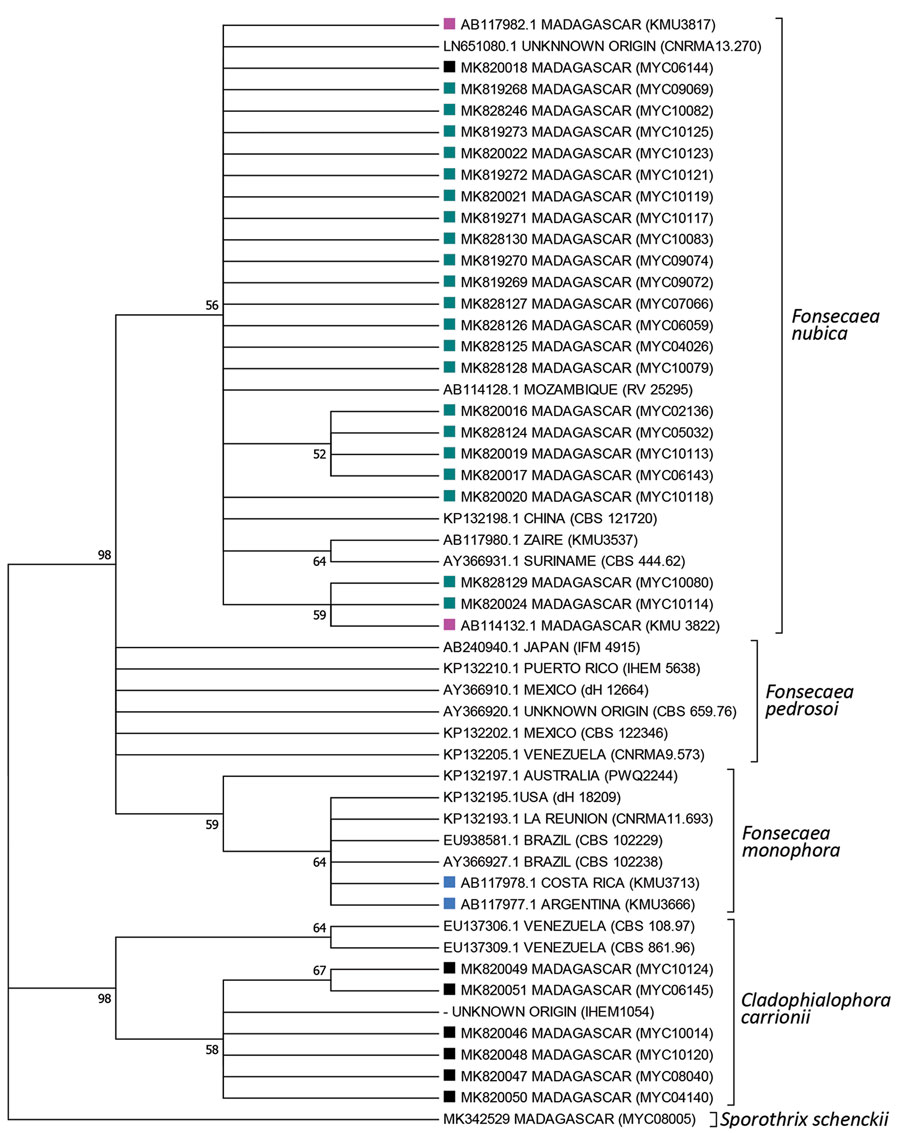
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of internal transcribed spacers sequences of fungal isolates from patients with chromoblastomycosis, Madagascar. Tree was constructed by using MEGA7.0 software (https://www.megasoftware.net) and applying the maximum-likelihood method based on the Kimura 2-parameter model (100 bootstrap replicates). Numbers along branches are bootstrap values. GenBank accession numbers are provided. Detailed information for strains is available (Appendix Table). Sporpthrix schenckii was used as the outgroup. Dark blue squares, Fonsecaea nubica sequences isolated in this study; black squares, Cladophialophora carrionii isolated in this study; pink squares, F. nubica previously identified as F. pedrosoi; light blue squares, F. monophora previously identified as F. pedrosi.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the 20th International Society for Human and Animal Mycology Conference; June 29–July 5, 2018; Amsterdam, the Netherlands.