Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Dispatch
Doxycycline and Sitafloxacin Combination Therapy for Treating Highly Resistant Mycoplasma genitalium
Figure
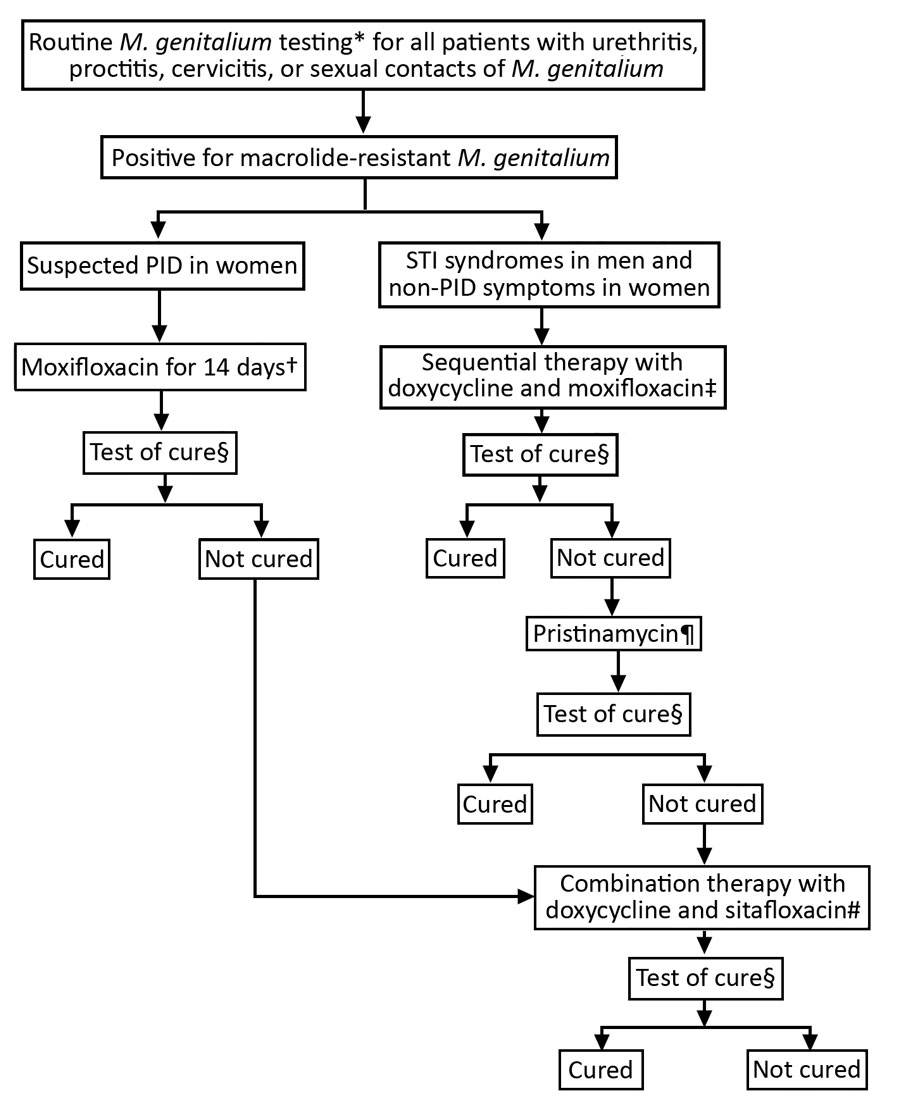
Figure. Clinical approach and treatment for patients with diagnosed macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium at Melbourne Sexual Health Centre, Australia. PID, pelvic inflammatory disease; STI, sexually transmitted infection. *Routine testing with the ResistancePlus MG assay (SpeeDx, https://plexpcr.com). †Moxifloxacin 400 mg/day for 14 days. ‡Doxycycline 100 mg 2 times/day for 7 days, then moxifloxacin 400 mg/d for 7 days. §Test of cure was recommended 14–28 days after completing antimicrobial treatment and all patients received a reminder. ResistancePlus MG Assay was used for all tests of cure. ¶When sequential therapy failed, patients were given a pristinamycin-based regimen for 10 days, either 1 g 4 times/day alone or 1 g 3 times/day in combination with doxycycline 100 mg 2 times/day. Doxycycline pretreatment also was given to some patients. #Doxycycline 100 mg and sitafloxacin 100 mg taken together 2 times/day for 7 days.