Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Synopsis
Pathology and Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with Fatal Coronavirus Disease, United States
Figure 3
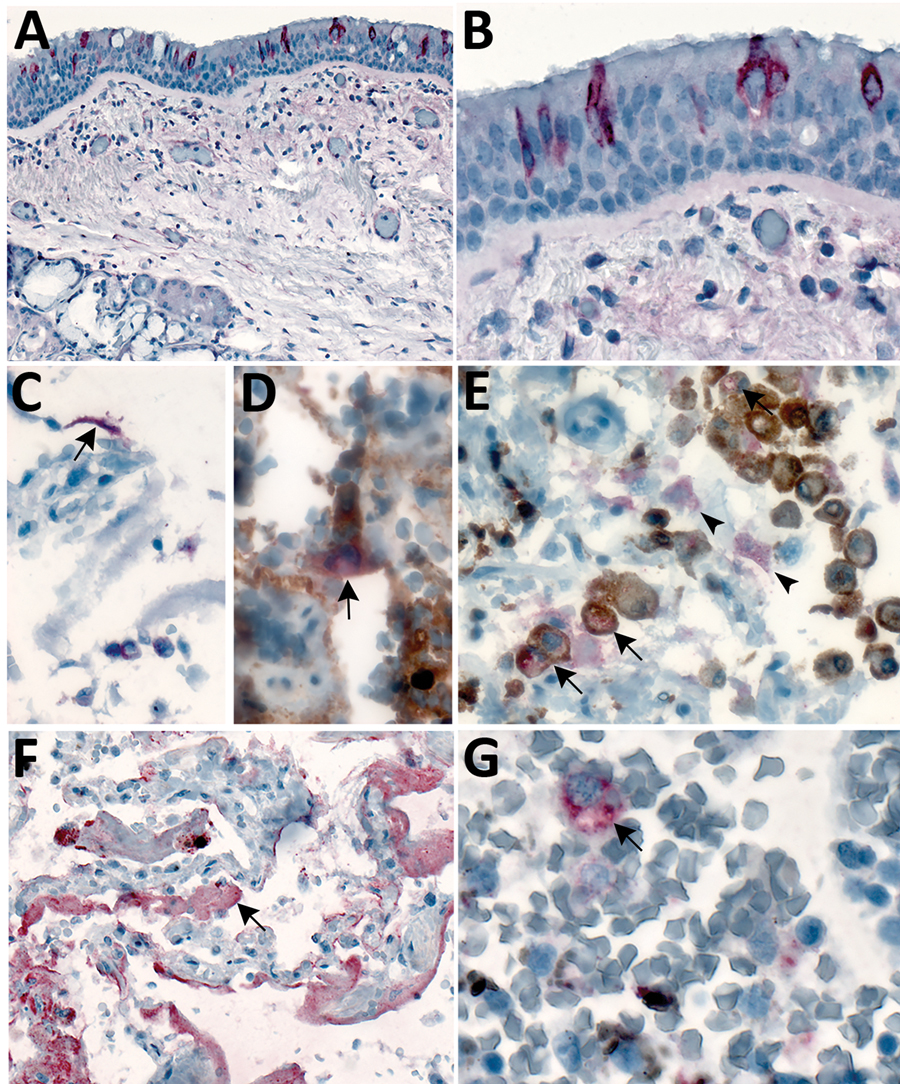
Figure 3. Immunostaining of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in pulmonary tissues from fatal coronavirus disease cases. A) Patient no. 5: scattered immunostaining of tracheal epithelial cells (original magnification ×40). B) Patient no. 5: higher magnification shows immunostaining of ciliated cells (original magnification ×63). C) Patient no. 8: immunostaining of desquamated type I pneumocyte in an alveolar lumen (original magnification ×63). D) Patient no. 4: colocalization of SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen (red) with type II pneumocyte stained by surfactant (brown; arrow) (original magnification ×63). E) Patient no. 4: colocalization of SARS-CoV-2 viral antigen (red) with macrophages stained by CD163 (brown; arrows); virus immunostaining within type II pneumocytes is also seen (arrowheads) (original magnification ×40). F) Patient no. 4: extensive immunostaining of hyaline membranes in a region of exudative DAD (original magnification ×20). G) Patient no. 3: scattered immunostaining within macrophage in hilar lymph node; anthracosis is also present (original magnification ×63).
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Members of the COVID-19 Pathology Working Group: Rhonda Cole, Amanda Lewis, Pamela Fair, Lindsey Estetter.