Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Synopsis
Pathology and Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with Fatal Coronavirus Disease, United States
Figure 4
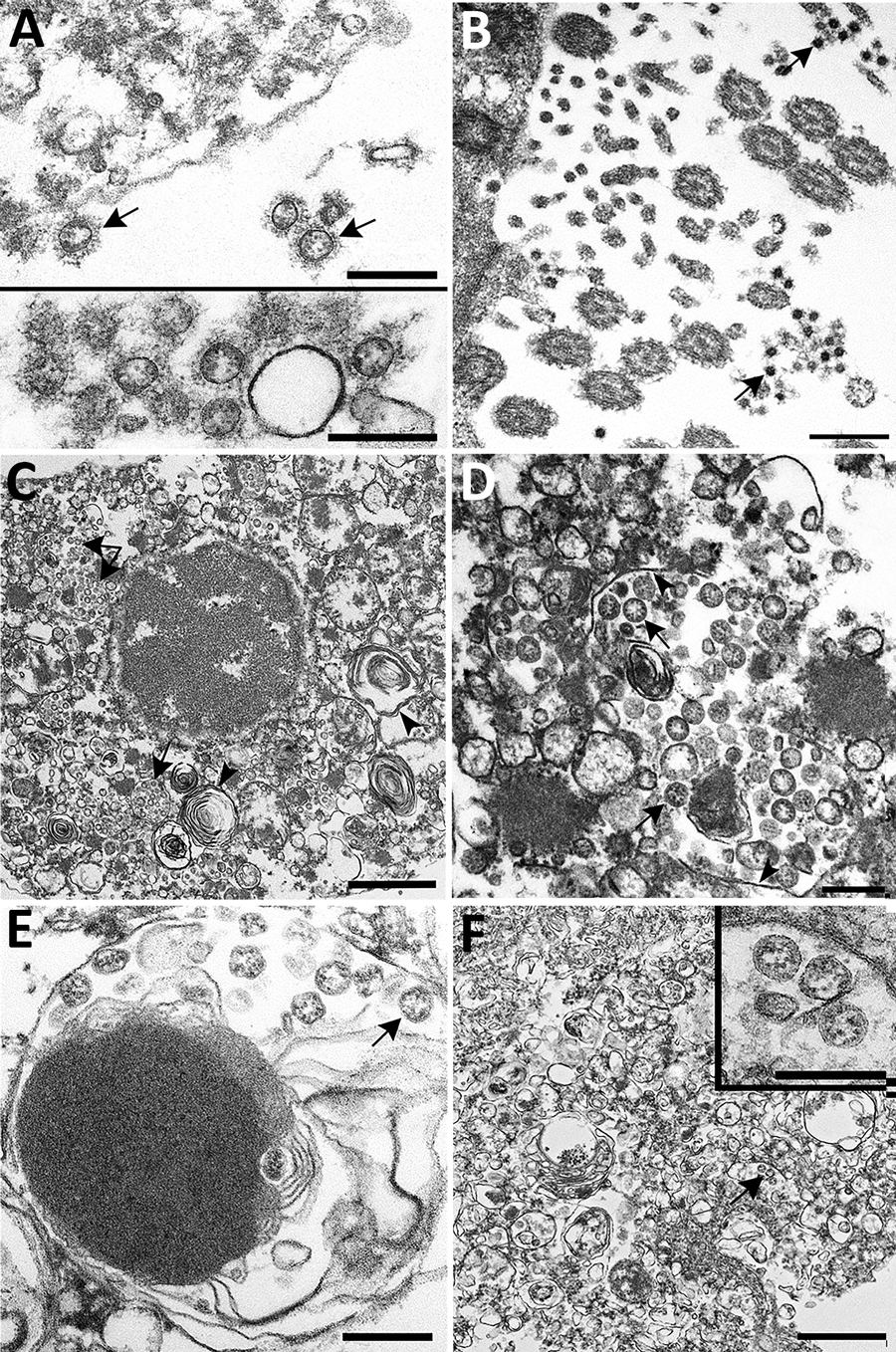
Figure 4. Ultrastructural features of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 lung infection in fatal coronavirus disease. A) Top: alveolar space containing extracellular virions (arrows) with prominent surface projections. Bottom: cluster of virions in the alveolar space. Scale bars indicate 200 nm. B) Extracellular virions (arrow) associated with ciliated cells of the upper airway. Scale bar indicates 200 nm. C) Membrane-bound vacuoles (arrows) containing viral particles within the cytoplasm of an infected type II pneumocyte; surfactant (lamellated material) indicted by arrowheads. Scale bar indicates 1 μm. D) Membrane-bound vacuole (double-headed arrow in panel C) containing virus particles (arrows) with the characteristic black dots that are cross-sections through the viral nucleocapsid. Arrowheads indicate vacuolar membrane. Scale bar indicates 200 nm. E) Viral particles (arrow) within a phagosome of an alveolar macrophage. Scale bar: 200 nm. F) Viral particles within a portion of a hyaline membrane. Scale bar indicates 800 nm. Inset: Higher magnification of virus particles indicated by arrow; scale bar indicates 200 nm.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Members of the COVID-19 Pathology Working Group: Rhonda Cole, Amanda Lewis, Pamela Fair, Lindsey Estetter.