Volume 27, Number 12—December 2021
Research
Novel Filoviruses, Hantavirus, and Rhabdovirus in Freshwater Fish, Switzerland, 2017
Figure 1
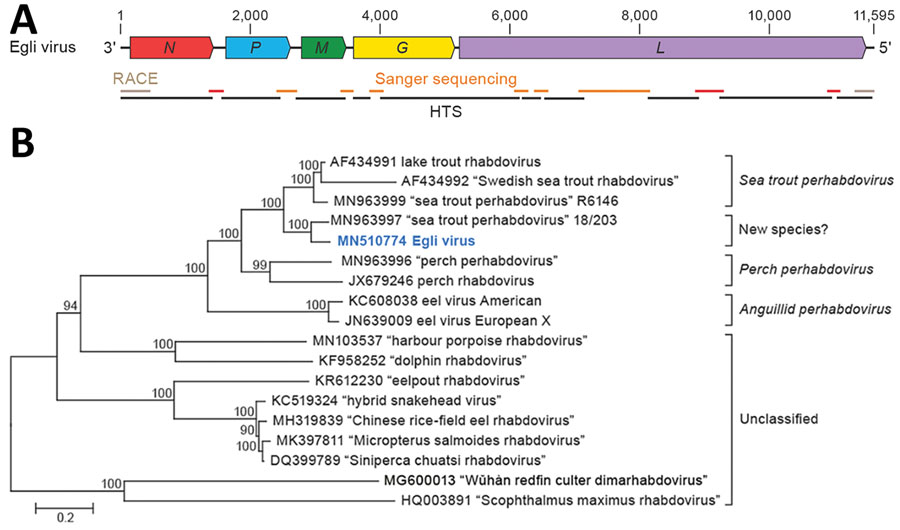
Figure 1. Identifying a novel rhabdovirus in European perch. A) Schematic representation of the EGLV genome organization; open reading frames are indicated by colored arrows. B) Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the nucleotide sequence of the EGLV L gene (bold blue) and representative classified and unclassified members of the genus Perhabdovirus. Numbers near nodes on the trees indicate bootstrap values. Branches are labeled by GenBank accession number and virus name. Names of unclassified likely perhabdoviruses are placed in quotation marks. Scale bar indicates number of substitutions per site, reflected by branch lengths. EGLV, Egli virus; G, glycoprotein gene; HTS, high-throughput sequencing; L, large protein gene; M, matrix protein gene; N, nucleoprotein gene; P, phosphoprotein gene; RACE, rapid amplification of cDNA ends.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.